Development and study of bioactive Ti + Mg composite BIACOM® for application of dental implants, the outputs of authors Martin Balog, Ahmed Mohamed Hassan Ibrahim, and Peter Krížik in the field of basic research: was selected for the annual report of SAS for the year 2020, as one of the most important outputs of the Scientific Section 1: Physical, Space, Earth, and Engineering Sciences.
From the prepared annual report of SAS:
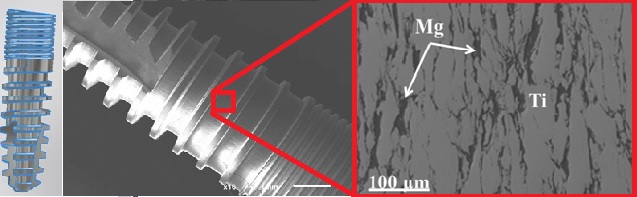
A unique partially biodegradable composite (BIACOM®) based on titanium (Ti) was produced as a material for use in prosthodontic surgery. BIACOM® is prepared by powder metallurgy approach, where a biodegradable component - magnesium (Mg) is added to the load-bearing matrix Ti structure in an optimal content of 17 vol.%, in the form of intentionally arrayed and interconnected microfibers. Owing to its specific fine-grained microstructure, the bioinert permanent Ti matrix controls the mechanical properties of the implant throughout its function in the human body. Thanks to the Mg component, BIACOM® minimizes the shortcomings of contemporary commercial Ti implants: i) the so-called shielding effect and ii) insufficient surface bioactivity. Mg lowers the Young's modulus (E) of BIACOM® and thus reduces the mechanical incompatibility of the implant with the bone. In addition, the Mg component degrades selectively and in a controlled manner upon the reaction of the implant in response with human body tissue and fluid, which is accompanied by the gradual formation of surface porosity. This leads to a further positive reduction in E, with the degraded Mg sites being gradually replaced by new tissue. In addition, the presence of Mg leads to improved osseointegrations and the subsequent formation of a good mechanical bond at the interface of the implant with the bone. At the same time, BIACOM® retains sufficient mechanical and fatigue properties, making it suitable for applications in which the implant is exposed to intense and cyclic mechanical stress, e.g., dental implants.
An in-vitro study of the response of 4 cell cultures to BIACOM® samples by indirect and direct contact methods indicated the need to stabilize the surface of BIACOM® due to the high degradation of Mg in the initial phase of exposure. Two different ways of stabilizing the surface of the BIACOM® samples were optimized, which led to the desired viability and cell proliferation, and a negative cytotoxic effect.
In cooperation with MARTIKAN s.r.o. a pilot batch of BIACOM® dental implants were CNC machined. According to the relevant standards for testing biomedical implants, these implants were subsequently tested with a positive result for fatigue life and in-vitro biological response.
Publications related to the project:
1. HASSAN IBRAHIM, Ahmed Mohamed - BALOG, Martin** - KRÍŽIK, Peter - NOVÝ, František - CETIN, Yuksel - ŠVEC, Peter, Jr. - BAJANA, Oto - DRIENOVSKÝ, Marián. Partially biodegradable Ti-based composites for biomedical applications subjected to intense and cyclic loading. In Journal of Alloys and Compounds. Vol. 839, (2020), s.1-13. ISSN 0925-8388 (2019: 4.650 - IF, Q1 - JCR Best Q, 1.055 - SJR, Q1 - SJR Best Q). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.155663
2. CETIN, Yuksel - HASSAN IBRAHIM, Ahmed Mohamed - GUNGOR, Aysen - YILDIZHAN, Yasemin - BALOG, Martin** - KRÍŽIK, Peter. In vitro evaluation of a partially biodegradable TiMg dental implant: The cytotoxicity, genotoxicity and oxidative stress. In Materialia. Vol. 14, (2020), s. 1-9. ISSN 2589-1529 (2019: 0.643 - SJR, Q2 - SJR Best Q). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtla.2020.100899
2. CETIN, Yuksel - HASSAN IBRAHIM, Ahmed Mohamed - GUNGOR, Aysen - YILDIZHAN, Yasemin - BALOG, Martin** - KRÍŽIK, Peter. In vitro evaluation of a partially biodegradable TiMg dental implant: The cytotoxicity, genotoxicity and oxidative stress. In Materialia. Vol. 14, (2020), s. 1-9. ISSN 2589-1529 (2019: 0.643 - SJR, Q2 - SJR Best Q). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtla.2020.100899