Advanced technologies /
General steps of pressure assisted liquid metal infiltration
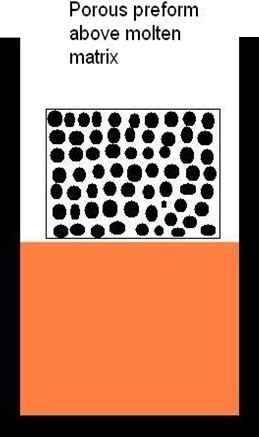
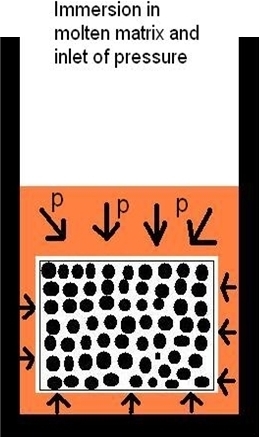
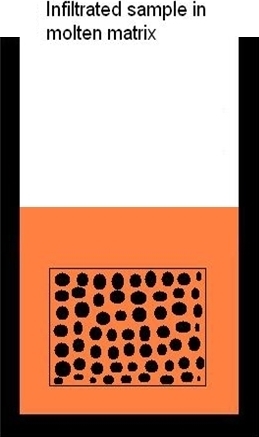
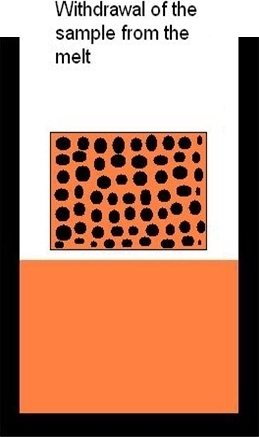
During infiltration the porous preform is held in the molten metal in an approximate holder. After infiltration samples are either pulled out from the melt or held in the molten matrix metal throughout the cooling cycle. Finally the infiltrated preform has to be machined-out form the metal volume.
Pressure assisted liquid metal infiltration makes the preparation of 3D composite parts possible. Limitations are given by the autoclave size and available heating. Various preforms can be prepared with different porosities. This determines the volume fractions of metal and reinforcing phase in the resulting composite.
The process is well manageable through main processing parameters i.e. temperature, gas pressure and time.
Monolayers of foils and wires are often prepared in advance using plasma spraying or diffusion bonding to fix the position of wires on the foil. In this case different orientation of fibres in 2D can be obtained.
The diffusion bonding is well manageable through main processing parameters i.e. temperature, pressure and time.
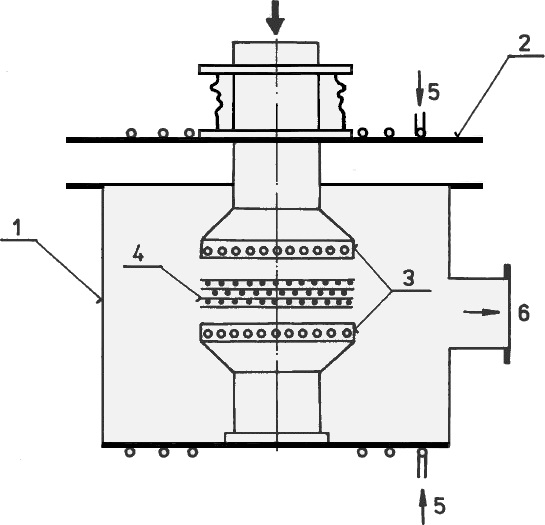 Vacuum chamber for diffusion bonding
Vacuum chamber for diffusion bonding
1 – vacuum chamber; 2 – lid, 3 – preheated pressing tool, 4 - composite perform, 5 – cooling water supply, 6 – vacuum pump connection
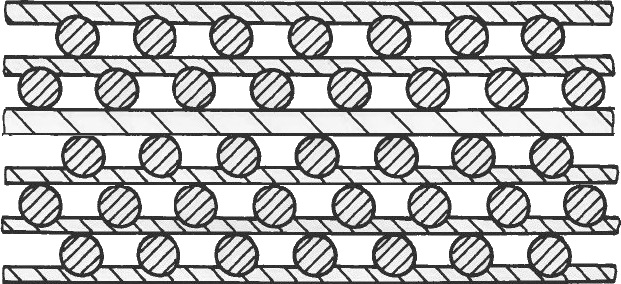 Preform of alternating layers of thin metal foils and wires
Preform of alternating layers of thin metal foils and wires
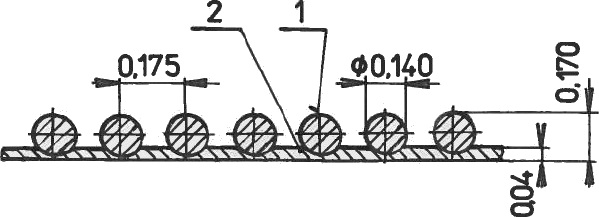 Monolayer of Al foils with B fibres prepared by diffusion bonding; 1 – B fibre, 2 – Al foil
Monolayer of Al foils with B fibres prepared by diffusion bonding; 1 – B fibre, 2 – Al foil
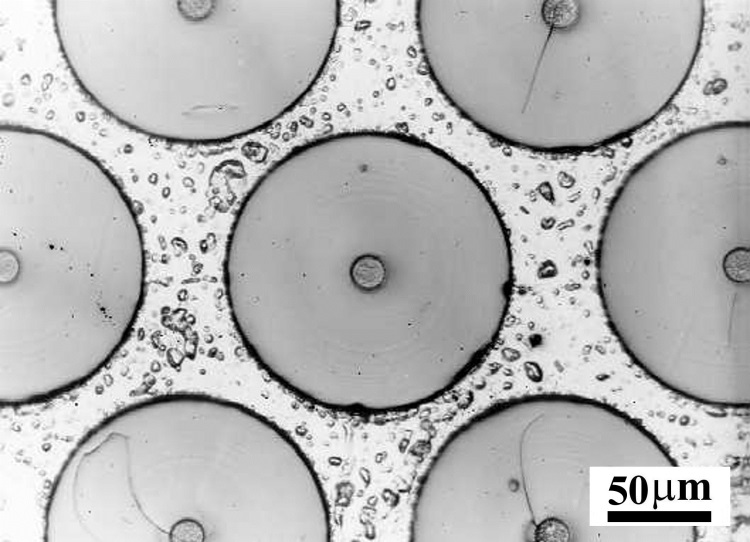 Aluminium matrix/boron fibre composite
Aluminium matrix/boron fibre composite
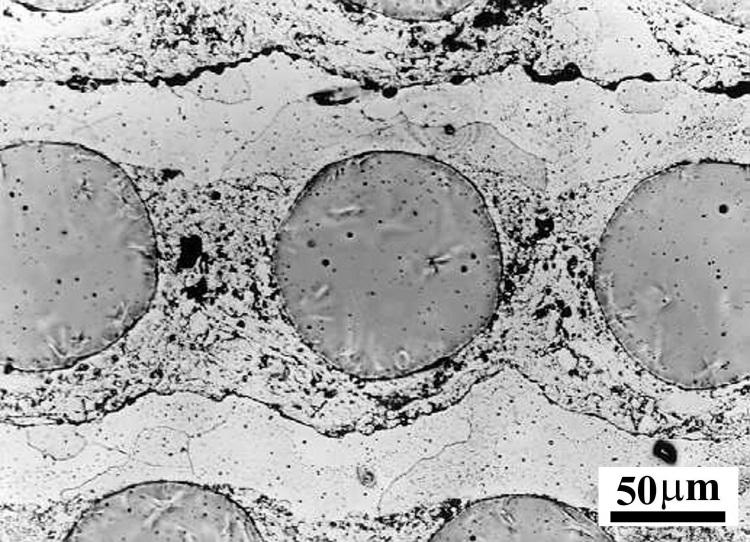 Aluminium matrix/steel wire composite
Aluminium matrix/steel wire composite
Manufacturing of metal matrix composites
Pressure assisted liquid metal infiltration
General description
Pressure assisted liquid metal infiltration is one of the cheapest and most easily applicable technologies for the production of metal matrix composites (MMCs).Principle of operation
Pressure assisted liquid metal infiltration is performed in autoclave where matrix metal is melted in graphite or steel crucible under vacuum. The molten metal is forced by the pressurized gas (up to 15 MPa) to penetrate into a porous ceramic or fibrous preform. External force has to be applied because most of liquid metals that are used for MMCs production do not wet the preforms sufficiently.General steps of pressure assisted liquid metal infiltration




During infiltration the porous preform is held in the molten metal in an approximate holder. After infiltration samples are either pulled out from the melt or held in the molten matrix metal throughout the cooling cycle. Finally the infiltrated preform has to be machined-out form the metal volume.
Pressure assisted liquid metal infiltration makes the preparation of 3D composite parts possible. Limitations are given by the autoclave size and available heating. Various preforms can be prepared with different porosities. This determines the volume fractions of metal and reinforcing phase in the resulting composite.
The process is well manageable through main processing parameters i.e. temperature, gas pressure and time.
Typical applications
The technique has been successfully applied for the preparation of:- copper matrix/graphite composites for sliding contacts in electrical vehicles
- copper matrix/alumina composites for break discs in automotive
- NiAl composites for intermetallic valves
- copper matrix/high modulus C fibres for heat sinks with high thermal conductivity
- aluminum matrix/high modulus C fibres for heat sinks with high thermal conductivity
- magnesium matrix/ C fibres for ultralight structural applications
- MgLi matrix/saffil composites for ultralight structural applications
- MgLi matrix /C fibres composites for ultralight structural applications
- Aluminum matrix/Al2O3 particles composites
Vacuum diffusion bonding
General description
Diffusion bonding is a solid state technique used for joining of metals or metals with ceramics, etc. It is widely used also for preparation of metal matrix composites (MMCs).Principle of operation
Diffusion bonding operates on the principle of solid state diffusion where the atoms of two solid surfaces intersperse themselves over time. This is usually implemented by applying high pressure, in conjunction with necessarily high temperature, to the materials to be bonded. The process is typically accomplished in vacuum chambers with preheated pressing tools. The technique is widely used to bond preforms of alternating layers of thin metal foils and metal wires or ceramic fibres.Monolayers of foils and wires are often prepared in advance using plasma spraying or diffusion bonding to fix the position of wires on the foil. In this case different orientation of fibres in 2D can be obtained.
The diffusion bonding is well manageable through main processing parameters i.e. temperature, pressure and time.
 Vacuum chamber for diffusion bonding
Vacuum chamber for diffusion bonding1 – vacuum chamber; 2 – lid, 3 – preheated pressing tool, 4 - composite perform, 5 – cooling water supply, 6 – vacuum pump connection
 Preform of alternating layers of thin metal foils and wires
Preform of alternating layers of thin metal foils and wires Monolayer of Al foils with B fibres prepared by diffusion bonding; 1 – B fibre, 2 – Al foil
Monolayer of Al foils with B fibres prepared by diffusion bonding; 1 – B fibre, 2 – Al foilTypical applications
The technique has been successfully applied for the preparation of- aluminium matrix/boron fibre composites
- aluminium matrix/steel wire composites.
 Aluminium matrix/boron fibre composite
Aluminium matrix/boron fibre composite Aluminium matrix/steel wire composite
Aluminium matrix/steel wire compositeEquipment
- 300 t hydraulic press
- vacuum chamber with preheated pressing tolls for samples up to 120 x 120 mm