Finite element analysis of mechanical behaviour of materials
Summary
Finite element analysis (FEA) is a numerical method used to simulate mechanical stresses, deformations, heat flows, vibrations and physical properties present in real materials, components or structures. The principle is based on subdivision of a real object into a large number of finite elements, such as little cubes, and surveyed parameters are determined in the individual grid points by mathematical equations. FEA has been used to analyse stress-strain fields developing during room temperature tensile testing of ferittic-pearlitic steel with a special attention given to their distribution in the necked region.Achievements
- The input data required for elastic-plastic model in FEA such as the Young's modulus, Poisson's ratio, true stress, true plastic strain, and strain hardening curve of the studied material were determined experimentally by the tensile tests. Figure shows the finite element meshes generated on the tensile specimens. For 3D analysis, the second-order tetrahedral elements with a size of 0.5 mm were used for the selected geometry of tensile specimens.
 Finite element tetrahedral mesh for cylindrical type of tensile specimen
Finite element tetrahedral mesh for cylindrical type of tensile specimen- Strain fields in x direction (εx) calculated by FEA indicating the local deformation along the gauge section of the hydrogenated and annealed specimens tested to fracture. Both figures clearly indicate highly non-uniform deformation with extensive necking characterised by a maximum local strain in the x direction for the specimen hydrogenated and annealed.
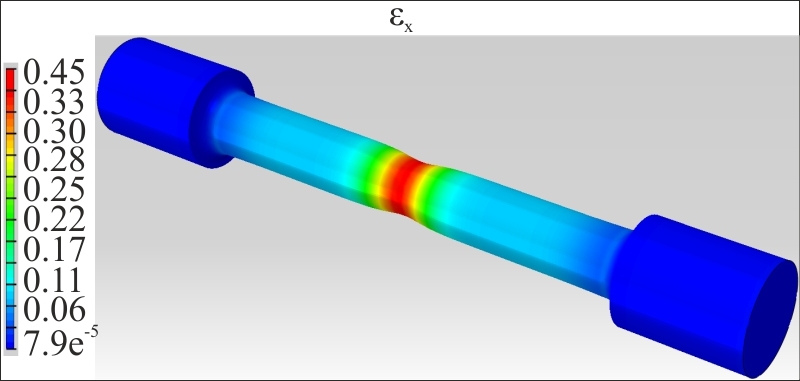 Calculated strain fields εx by the FEA method for hydrogenated specimen
Calculated strain fields εx by the FEA method for hydrogenated specimen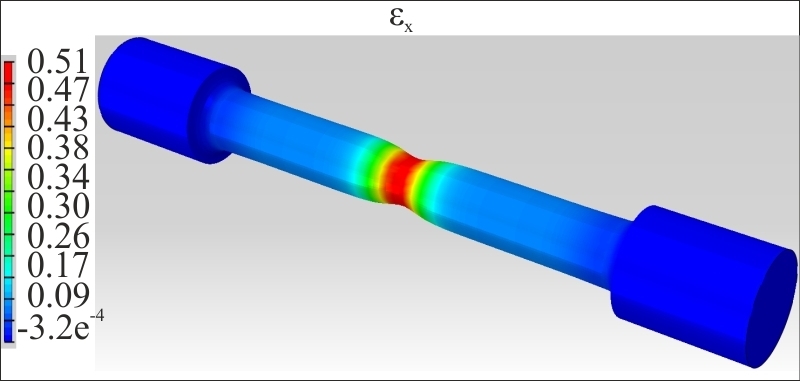 Calculated strain fields εx by the FEA method for annealed specimen
Calculated strain fields εx by the FEA method for annealed specimenAdditional reading
ŠTAMBORSKÁ, M. – LAPIN, J. – BAJANA, O. – LOSERTOVÁ, M. Tensile deformation behavior of ferritic-pearlitic steel studied by digital image correlation method. In Kovové materiály, 2015, Vol. 53, No. 6, p. 399-407. (Current Contents, Scopus, WOS). ISSN 0023-432X.ŠTAMBORSKÁ, M. – LAPIN, J. – BAJANA, O. Effect of hydrogenation on deformation behaviour of ferritic-pearlitic steel studied by digital image correlation method. In Kovové materiály, 2016, Vol. 54, No. 6, pp.397-406. (Current Contents, Scopus, WOS). ISSN 0023-432X.
Related projects
- Research center ALLEGRO, 2014 - 2015
- Investment casting of turbine blades from nickel based superalloys, 2013 - 2016
- New high temperature composite materials for turbochargers, 2016 - 2020