Advanced studies /
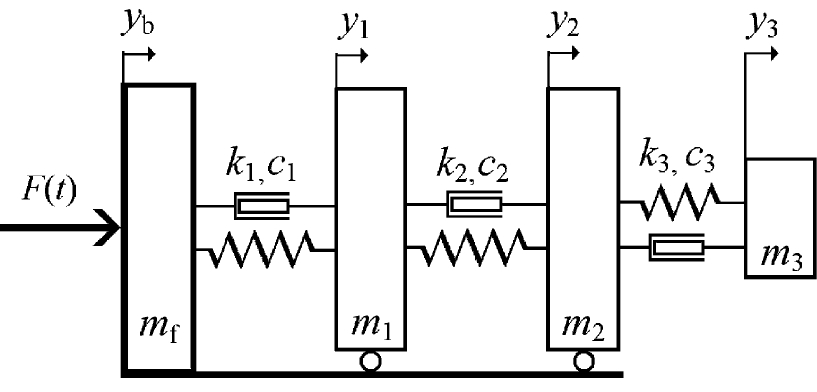 Model of the seated human body and cushioned seat in the lateral direction
Model of the seated human body and cushioned seat in the lateral direction
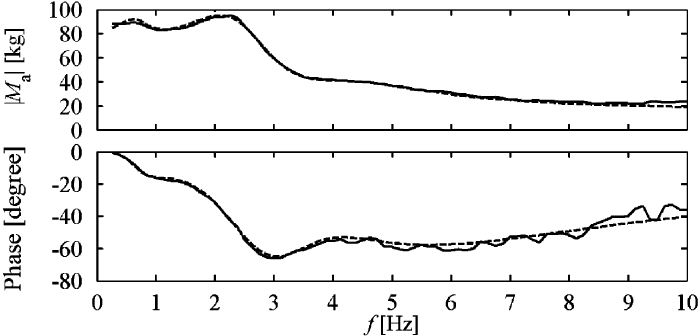 Simulated (solid) and mean measured (dashed) apparent mass modulus and phase for excitation intensity e2 = 0.98 m/s2
Simulated (solid) and mean measured (dashed) apparent mass modulus and phase for excitation intensity e2 = 0.98 m/s2
STEIN, George Juraj - MÚČKA, Peter - CHMÚRNY, Rudolf. Preliminary results on an x-direction apparent mass model of human body sitting in a cushioned, suspended seat. In Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2006, vol. 298, p. 688-703. ISSN 0022-460 X.
STEIN, George Juraj - MÚČKA, Peter - CHMÚRNY, Rudolf - HINZ, Barbara - BLÜTHNER, Ralph. Measurement and modelling of x-direction apparent mass of the seated human body-cushioned seat system. In Journal of Biomechanics, 2007, vol. 40, p.1493-1503. (2007 - Current Contents). ISSN 0021-9290.
STEIN, George Juraj - MÚČKA, Peter - GUNSTON, T.P. - BADURA, S. Modelling and simulation of locomotive driver's seat vertical suspension vibration isolation system. In International Journal of Industrial Ergonomics, 2008, vol. 38, nos.5-6, p.384-395. (2008 - Current Contents). ISSN 0169-8141.
STEIN, George Juraj - ZAHORANSKÝ, Radúz - MÚČKA, Peter. On dry friction modelling and simulation in kinematically excited oscillatory systems. In Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2008, vol. 311, p.74-96. (1.024 - IF2007). (2008 - Current Contents). ISSN 0022-460X.
STEIN, G. J. – ZAHORANSKÝ, R. – GUNSTON, T. P. – BURSTRÖM, L. – MEYER, L. Modelling and simulation of a fore-and-aft driver’s seat suspension system with road excitation. In International Journal of Industrial Ergonomics. Vol. 38, nos. 5-6 (2008),p. 396-409. (CC) (0,628 - IF 2007)
STEIN, George Juraj - MÚČKA, Peter - GUNSTON, T.P. A study of locomotive driver´s seat vertical suspension system with adjustable damper. In Vehicle System Dynamics, 2009, vol. 47, no.3, p.363-386. (0.724 - IF2008). (2009 - Current Contents). ISSN 0042-3114.
STEIN, George Juraj - MÚČKA, Peter - HINZ, Barbara - BLÜTHNER, Ralph. Measurement and modelling of the y-direction apparent mass of sitting human body-cushioned seat system. In Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2009, vol. 322, nos.1-2, p. 454-474. (1.364 - IF2008). ISSN 0022-460X.
STEIN, George Juraj - MÚČKA, Peter. Study of simultaneous shock and vibration control by a fore-and-aft suspension system of a driver´s seat. In International Journal of Industrial Ergonomics, 2011, vol. 41, p.520-529. (1.322 - IF2010). (2011 - Current Contents). ISSN 0169-8141.
STEIN, George Juraj - CHMÚRNY, Rudolf - ROSÍK, Vladimír. Compact Vibration Measuring System for in-vehicle Applications. In Measurement Science Review : 2011, vol.11, no.5, p.154-159. (0.400 - IF2010). (2011 - WOS, SCOPUS). ISSN 1335-8871.
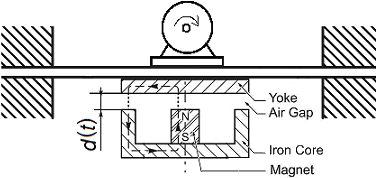 Schematic layout of the damping device in conjunction with the machine frame.
Schematic layout of the damping device in conjunction with the machine frame.
The central magnetic flux line is denoted dashed.
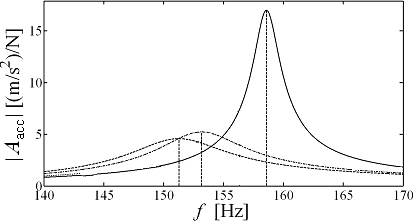 Measured accelerance of oscillatory system without the damping device (bold) and with the influence of the damping device with different air gap width d0 (dashed and dotted). Note the decrease of amplitude of the resonance peak by 70 % of the original value and decrease in resonance frequency up to 4 %.
Measured accelerance of oscillatory system without the damping device (bold) and with the influence of the damping device with different air gap width d0 (dashed and dotted). Note the decrease of amplitude of the resonance peak by 70 % of the original value and decrease in resonance frequency up to 4 %.
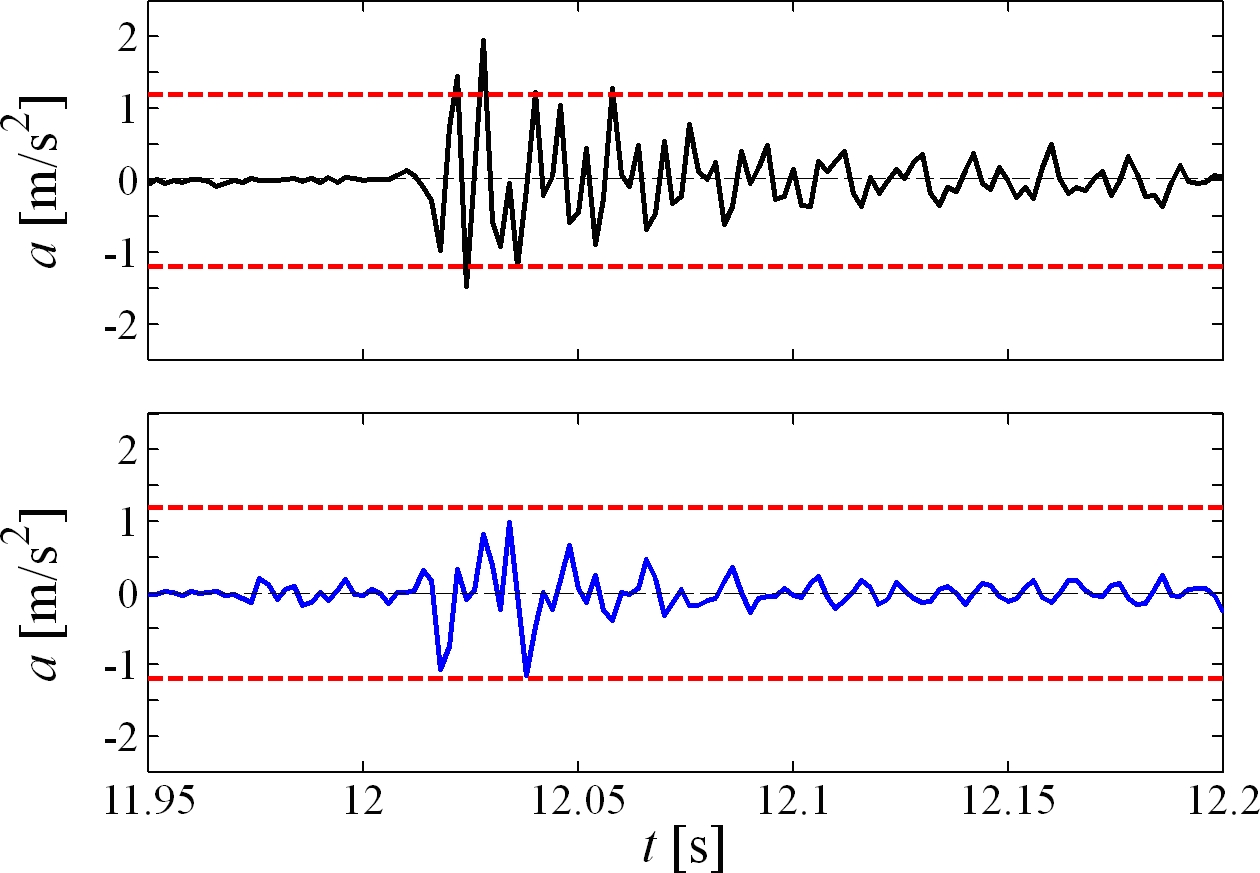 Run up of the rotating machine, passing the frame resonance: without the influence of the damping device (upper figure) and with the action of the damping device (lower figure). Note that the set limits on peak vibration acceleration are not surpassed in the second figure.
Run up of the rotating machine, passing the frame resonance: without the influence of the damping device (upper figure) and with the action of the damping device (lower figure). Note that the set limits on peak vibration acceleration are not surpassed in the second figure.
STEIN, George Juraj - TOBOLKA, Peter - CHMÚRNY, Rudolf. Ferromagnetic eddy current damper of beam transversal vibrations. Journal of Vibration and Control, 2016. DOI: 10.1177/1077546316654791 (in press)
STEIN, George Juraj - TOBOLKA, Peter - CHMÚRNY, Rudolf. Preliminary investigations of machine frame vibration damping using eddy current principle. Applied Mechanics and Materials, Vol. 821, 2016, Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland, pp. 288-294. doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMM.821.288. (Scopus)
STEIN, Juraj - CHMÚRNY, Rudolf. Natural frequencies of classical clamped-clamped beam with a concentrated load at its mid-point. Asian Journal of Mathematics and Computer Research, ISSN 2395-4205, Vol. 8, 2016, No.1, pp. 69-81.
Vibroinsulation
Improvement of suspension seat performance
Summary
The objectives were to improve understanding of the dynamic behaviour of suspension seats in response to translational and rotational motions and to develop theoretical and physical suspension systems capable of improving seat performance in these axes.Objectives
The research activities were mainly devoted to:- assessment of the dynamic performance of representative suspension seats in the fore-and-aft and lateral directions in the laboratory
- development of mathematical models for simulation of the seat-person system dynamic performance in both horizontal directions
- determination of seat component dynamic properties
- development of improved horizontal seat suspension systems using the mathematical models
Achievements
- model of the seated human body and cushioned seat in the fore-and-aft direction has been developed (Stein et al. JoB 2007; Stein et al. JSV 2006);
- model of the seated human body and cushioned seat in the lateral direction was developed (Stein et al. JSV 2009);
- model of the locomotive seat vertical suspension was proposed to predict vibration influence on driver under field conditions (Stein et al. IJIE 2008);
- model of the locomotive seat vertical suspension with optimised adjustable damper was proposed (Stein et al. VSD 2009);
- methodology of physically correct stick–slip model of dry-friction in oscillatory system was proposed (Stein et al. JSV 2008);
- design and manufacturing of a compact vibration measuring system of human vibration influence based on 3D MEMS accelerometers.
 Model of the seated human body and cushioned seat in the lateral direction
Model of the seated human body and cushioned seat in the lateral direction Simulated (solid) and mean measured (dashed) apparent mass modulus and phase for excitation intensity e2 = 0.98 m/s2
Simulated (solid) and mean measured (dashed) apparent mass modulus and phase for excitation intensity e2 = 0.98 m/s2Additional reading
STEIN, George Juraj - MÚČKA, Peter. Theoretical investigation of a linear planar model of a passenger car with seated people. In Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers Part D : Journal of Automobile Engineering, 2003, vol. 217, p. 257-268.STEIN, George Juraj - MÚČKA, Peter - CHMÚRNY, Rudolf. Preliminary results on an x-direction apparent mass model of human body sitting in a cushioned, suspended seat. In Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2006, vol. 298, p. 688-703. ISSN 0022-460 X.
STEIN, George Juraj - MÚČKA, Peter - CHMÚRNY, Rudolf - HINZ, Barbara - BLÜTHNER, Ralph. Measurement and modelling of x-direction apparent mass of the seated human body-cushioned seat system. In Journal of Biomechanics, 2007, vol. 40, p.1493-1503. (2007 - Current Contents). ISSN 0021-9290.
STEIN, George Juraj - MÚČKA, Peter - GUNSTON, T.P. - BADURA, S. Modelling and simulation of locomotive driver's seat vertical suspension vibration isolation system. In International Journal of Industrial Ergonomics, 2008, vol. 38, nos.5-6, p.384-395. (2008 - Current Contents). ISSN 0169-8141.
STEIN, George Juraj - ZAHORANSKÝ, Radúz - MÚČKA, Peter. On dry friction modelling and simulation in kinematically excited oscillatory systems. In Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2008, vol. 311, p.74-96. (1.024 - IF2007). (2008 - Current Contents). ISSN 0022-460X.
STEIN, G. J. – ZAHORANSKÝ, R. – GUNSTON, T. P. – BURSTRÖM, L. – MEYER, L. Modelling and simulation of a fore-and-aft driver’s seat suspension system with road excitation. In International Journal of Industrial Ergonomics. Vol. 38, nos. 5-6 (2008),p. 396-409. (CC) (0,628 - IF 2007)
STEIN, George Juraj - MÚČKA, Peter - GUNSTON, T.P. A study of locomotive driver´s seat vertical suspension system with adjustable damper. In Vehicle System Dynamics, 2009, vol. 47, no.3, p.363-386. (0.724 - IF2008). (2009 - Current Contents). ISSN 0042-3114.
STEIN, George Juraj - MÚČKA, Peter - HINZ, Barbara - BLÜTHNER, Ralph. Measurement and modelling of the y-direction apparent mass of sitting human body-cushioned seat system. In Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2009, vol. 322, nos.1-2, p. 454-474. (1.364 - IF2008). ISSN 0022-460X.
STEIN, George Juraj - MÚČKA, Peter. Study of simultaneous shock and vibration control by a fore-and-aft suspension system of a driver´s seat. In International Journal of Industrial Ergonomics, 2011, vol. 41, p.520-529. (1.322 - IF2010). (2011 - Current Contents). ISSN 0169-8141.
STEIN, George Juraj - CHMÚRNY, Rudolf - ROSÍK, Vladimír. Compact Vibration Measuring System for in-vehicle Applications. In Measurement Science Review : 2011, vol.11, no.5, p.154-159. (0.400 - IF2010). (2011 - WOS, SCOPUS). ISSN 1335-8871.
Related projects
- Evaluation and improvement of suspension seat vibration isolation performance, 2002 - 2005
- Vibration mitigation of driver-operator in fore-and-aft direction by passive, active or semi-active vibration control systems, 2006 - 2008
- Vibration mitigation of the vehicle driver/operator in two directions (axis) by passive, active or semi-active vibration control systems while accounting for properties of real excitation from road, terrain and driving unit, 2010 - 2012
Novel electro-magnetic vibration damper based on the eddy current principle
Summary
Novel electro-magnetic damper, based on the eddy current principle was developed. Instead of commonly used good conducting material (e.g. copper) a ferro magnetic yoke is used, which, except of damping of the resonance vibrations facilitates shift of the resonance frequency to lower frequencies. Both features are advantageous in vibration control, especially of light-weighted frames of rotating machines.Working principle
The rotating machine is situated on a flexible frame (raft), to which a ferromagnetic yoke is fixed. Below the yoke a rotationally symmetric pot-type iron core is situated. In the centre of the pot core, an axially polarized permanent magnet is situated. The yoke is axially vibrating in the vertical direction; hence there is a variable air gap of width d(t). Schematic layout of the damping device in conjunction with the machine frame.
Schematic layout of the damping device in conjunction with the machine frame.The central magnetic flux line is denoted dashed.
Three magnetic forces are acting in the oscillatory system:
The static magnetic force is counterbalanced by the frame stiffness so that the static distance is d0. There is a lower limit on the static distance d0, because if the static magnetic force would overwhelm the elastic forces the yoke would be fully attracted to the core and any oscillations would extinct.
The dynamic magnetic force due to yoke vibration in the static magnetic field of the permanent magnet generates a dynamic force counteracting the force due to frame stiffness and in this way decreases the overall oscillatory system stiffness, leading to decrease in the resonance frequency.
The magnetic force exerted by the eddy current circulating in the yoke depends on the properties of the magnetic circuit. It introduces additional damping into the oscillatory system.
The static magnetic force is counterbalanced by the frame stiffness so that the static distance is d0. There is a lower limit on the static distance d0, because if the static magnetic force would overwhelm the elastic forces the yoke would be fully attracted to the core and any oscillations would extinct.
The dynamic magnetic force due to yoke vibration in the static magnetic field of the permanent magnet generates a dynamic force counteracting the force due to frame stiffness and in this way decreases the overall oscillatory system stiffness, leading to decrease in the resonance frequency.
The magnetic force exerted by the eddy current circulating in the yoke depends on the properties of the magnetic circuit. It introduces additional damping into the oscillatory system.
Performance
The performance of the damping device can be illustrated on hand of following figures: Measured accelerance of oscillatory system without the damping device (bold) and with the influence of the damping device with different air gap width d0 (dashed and dotted). Note the decrease of amplitude of the resonance peak by 70 % of the original value and decrease in resonance frequency up to 4 %.
Measured accelerance of oscillatory system without the damping device (bold) and with the influence of the damping device with different air gap width d0 (dashed and dotted). Note the decrease of amplitude of the resonance peak by 70 % of the original value and decrease in resonance frequency up to 4 %. Run up of the rotating machine, passing the frame resonance: without the influence of the damping device (upper figure) and with the action of the damping device (lower figure). Note that the set limits on peak vibration acceleration are not surpassed in the second figure.
Run up of the rotating machine, passing the frame resonance: without the influence of the damping device (upper figure) and with the action of the damping device (lower figure). Note that the set limits on peak vibration acceleration are not surpassed in the second figure.Selected publications
Patent application No. PP50072-2014 “Magnetický tlmič vibrácií, pracujúci na báze vírivých prúdov a jeho umiestnenie v kmitavej sústave”, 2014, Indrustrial Property Office of the Slovak Republic.STEIN, George Juraj - TOBOLKA, Peter - CHMÚRNY, Rudolf. Ferromagnetic eddy current damper of beam transversal vibrations. Journal of Vibration and Control, 2016. DOI: 10.1177/1077546316654791 (in press)
STEIN, George Juraj - TOBOLKA, Peter - CHMÚRNY, Rudolf. Preliminary investigations of machine frame vibration damping using eddy current principle. Applied Mechanics and Materials, Vol. 821, 2016, Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland, pp. 288-294. doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMM.821.288. (Scopus)
STEIN, Juraj - CHMÚRNY, Rudolf. Natural frequencies of classical clamped-clamped beam with a concentrated load at its mid-point. Asian Journal of Mathematics and Computer Research, ISSN 2395-4205, Vol. 8, 2016, No.1, pp. 69-81.