Degradation of microstructure and mechanical properties of single crystalline nickel based superalloys
Characterization
Nickel base superalloys are widely used as high-temperature structural materials because of their unusual ability to retain excellent combinations of mechanical properties and corrosion resistance at high temperatures comparing with other materials, such as titanium base alloys, iron base alloys or structural ceramics. Their application temperatures are relatively high and often exceed 0.7 of their melting temperature. Different generations of nickel based superalloys differ in content of refractory elements. In industry, nickel based single crystal superalloys of the 2nd and the 3rd generations areused in aircraft and power engineering for manufacturing the first stage blades for gasturbines on a large scale. CMSX-4 is typical representative of the 2nd generation containing 3 wt. % of Re.Objectives
- To study microstructural stability of CMSX4 superalloy during long term high temperature exposure.
- To determine the effect of microstructure degradation on the mechanical properties.
- To study theeffect of uniaxial stress state conditions on microstructure degradation.
- To study theeffect of multiaxial stress state conditions on microstructuredegradation.
- Case studies.
Achievements
- Two basic types of microstructure degradation are observed after long-term ageing: coarsening of the cuboidal γ’ precipitates and formation of spontaneously rafted microstructure.
- During service the initial microstructure of single crystal blades is subjected to degradation by the combined effect of temperature, mechanical stresses and environmental conditions. Three types of microstructure degradation can be observed: (i) growth of γ’ precipitates; (ii) spontaneous rafting formed preferentially within the dendrites during long-term ageing and (iii) creep rafting.
- The initial cuboidal γ/γ’ microstructure of single crystal CMSX-4 superalloy is unstable during 950 °C creep at uniaxial stress conditions. The width of the γ’(Ni3(Al,Ti)) rafts decreases and length of the γ’ rafts and width of the γ channels increase with increasing applied stress and creep time during tensile creep testing.
- For the multiaxial stress conditions, there is no evidence of directional coarsening of the cuboidal γ/γ’ microstructure within the region affected by maximal principal stresses. Fully rafted microstructure with the rafts oriented perpendicularly to the [001] crystallographic direction is observed within the region affected primarily by maximal principal stresses, where the stress intensity and compressive stresses have negligible magnitudes. Non-uniform directional coarsening of the γ’ phase is observed within the region, where beside the effect of maximal principal stresses, the non-negligible compressive stresses takes place.
- The external stress of about 50 MPa resulting from centrifugal forces during blade service is determined to be critical for formation of spontaneously rafted microstructure. Higher stresses leads to fully rafted or partially rafted microstructure depending on local temperature within the turbine blade.
SEM micrographs showing the effect of ageing on morphology of cuboidal γ` precipitates
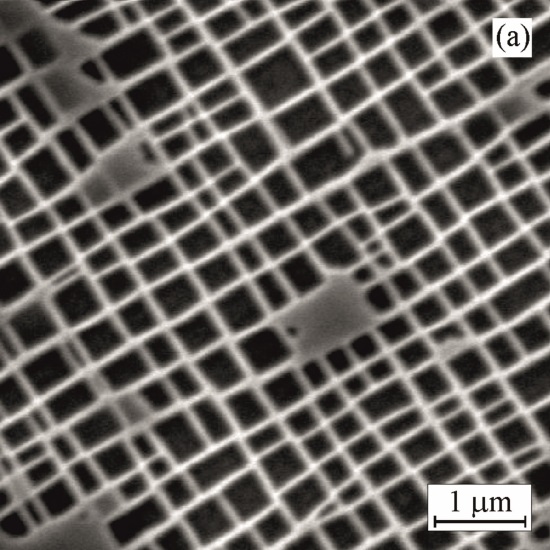 Initial, before ageing
Initial, before ageing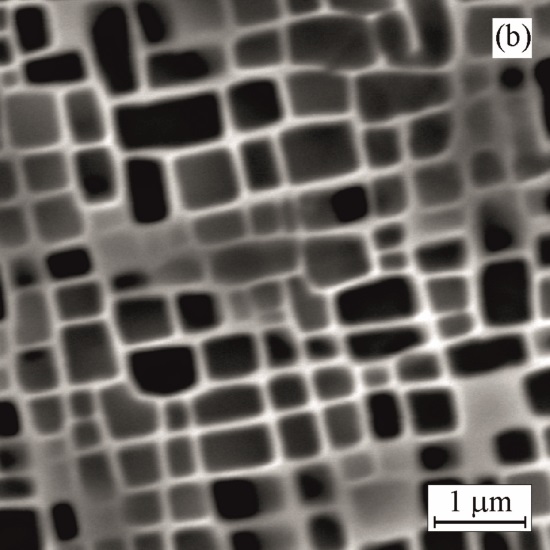 Ageing at 950°C for 500 h
Ageing at 950°C for 500 h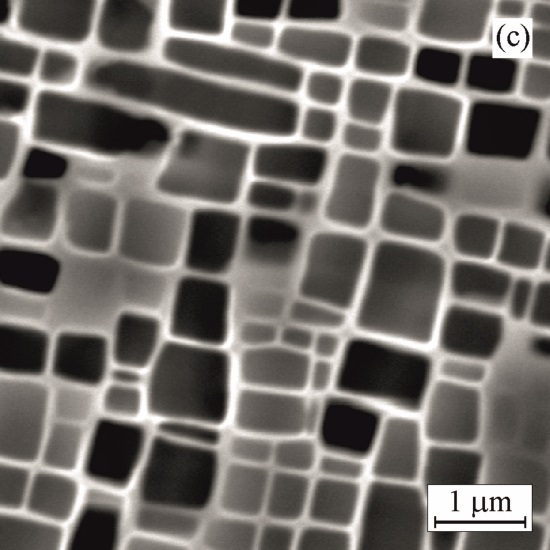 Ageing at 950°C for 1000 h
Ageing at 950°C for 1000 h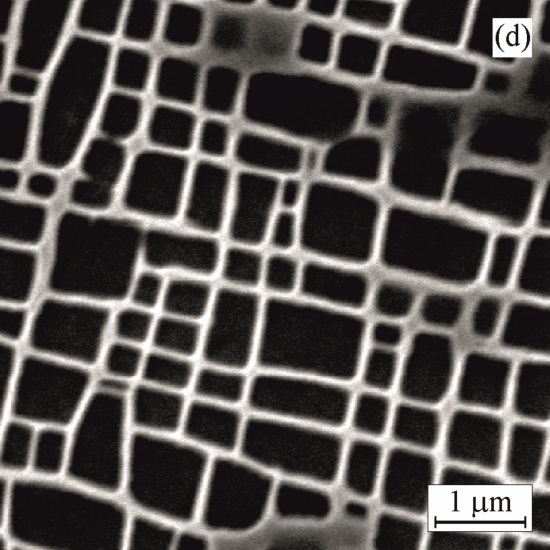 Ageing at 950°C for 2000 h
Ageing at 950°C for 2000 h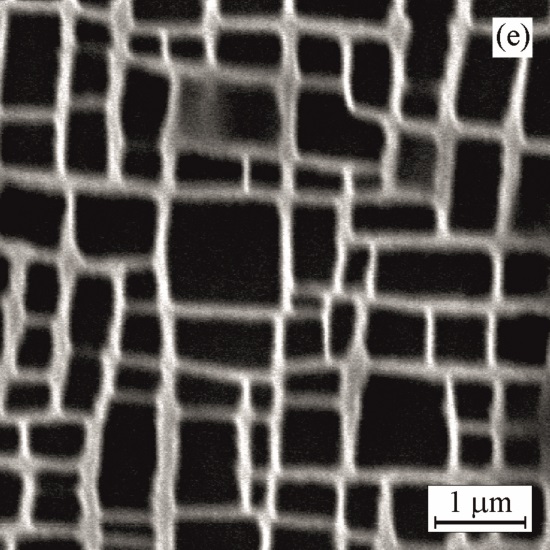 Ageing at 1000°C for 500 h
Ageing at 1000°C for 500 h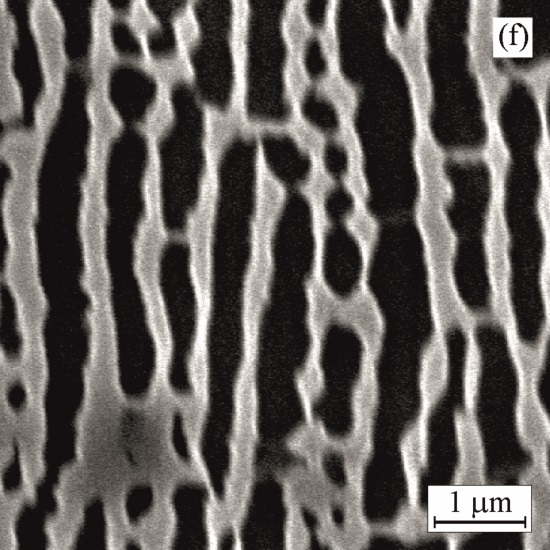 Ageing at 1000°C for 1000 h
Ageing at 1000°C for 1000 h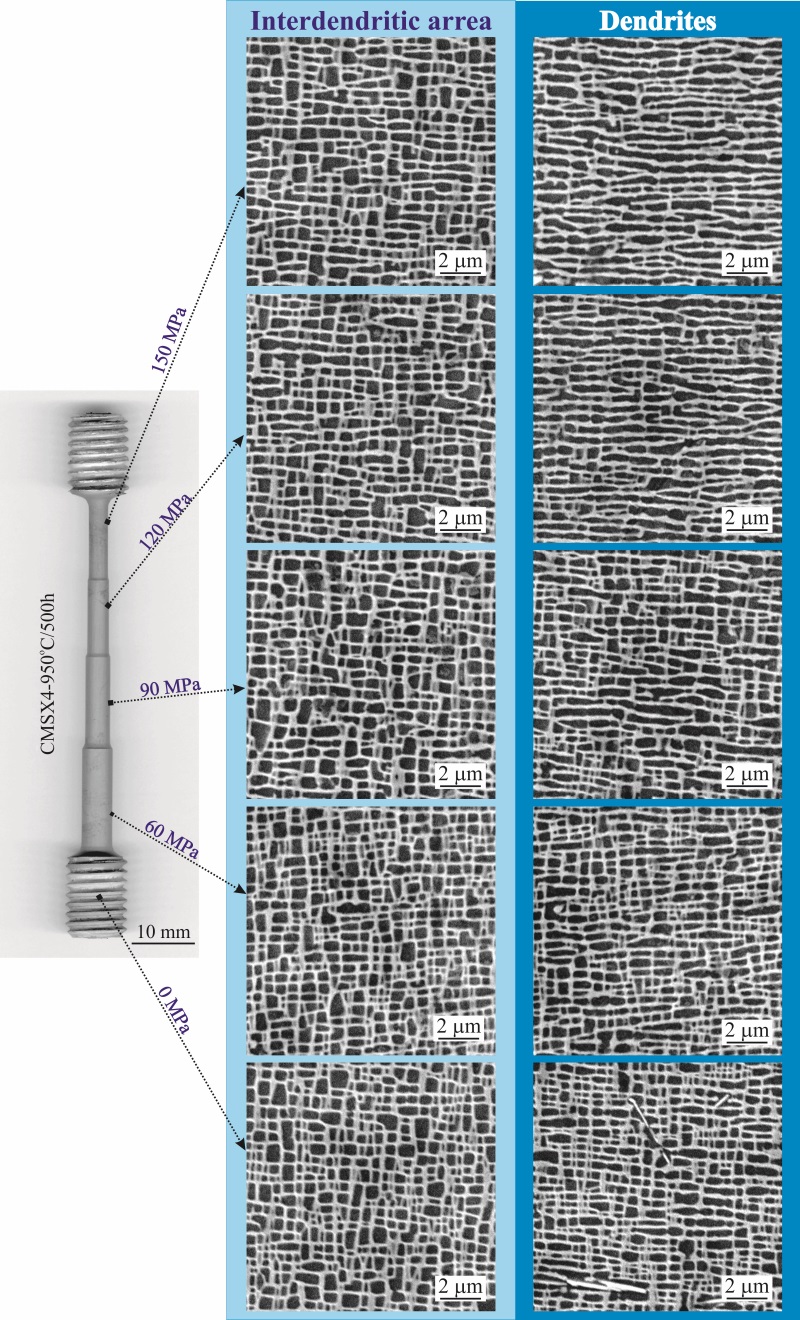
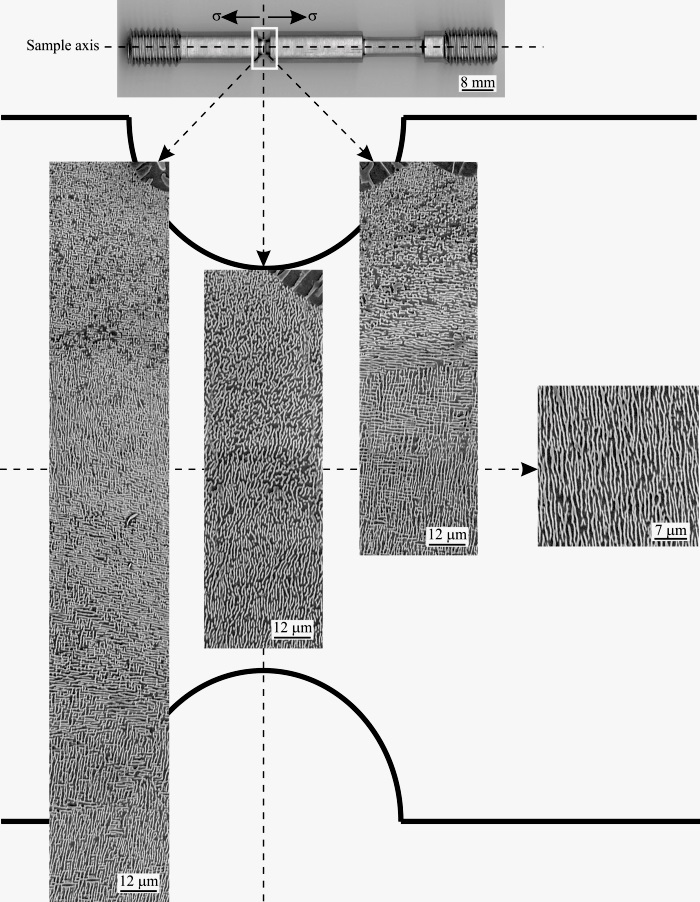
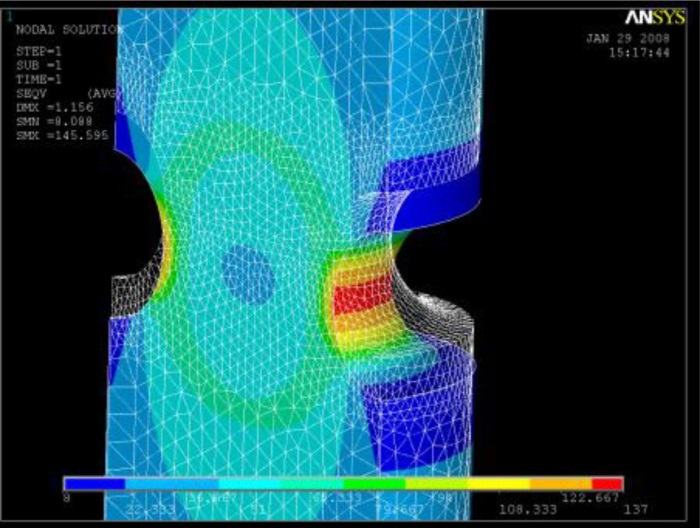 Calculated distribution of Von Mises stresses in the notch affected region of the creep specimen
Calculated distribution of Von Mises stresses in the notch affected region of the creep specimenAdditional reading
LAPIN, J. - PELACHOVÁ, T. - GEBURA, M. The effect of creep exposure on microstructure stability and tensile properties of single crystal nickel based superalloy CMSX-4. In KOVOVE MATER, 2012, vol.50, pp. 379-386. (IF 0.687) (Current Contents, Scopus, WOS). ISSN 0023-432X.LAPIN, J. - PELACHOVÁ, T. - GEBURA, M. Microstructure degradation of nickel based single crystal superalloy during creep. In 21st International Conference on Metallurgy and Materials, METAL 2012. 2012, Tanger Ltd, pp. 1257-1263. (Scopus, WOS). ISBN 978-80-87294-31-4.
GEBURA, M. - LAPIN, J. The Effect of Multiaxial Stress State on Formation of Rafts in CMSX-4 Superalloy during Creep. In ADV MAT RES., 2011, vol.278,pp. 222-227. (Scopus, WOS). ISSN print 1022-6680.
GEBURA, M. - LAPIN, J. The effect of multiaxial stress state on rafting in CMSX-4 superalloy during creep. In TECHNOLÓGIA 2011, 2011, Ed.: Hrnčiar, V., Bratislava, STU, pp. 44-50. ISBN 978-80-227-3545-2.
GEBURA, M. - LAPIN, J. Microsegregation Induced Inhomogeneity of Coarsening of γ´ Precipitates in a Nickel-based Single Crystal Superalloy. In DEFECT DIFFUS FORUM, 2010, vols.297-301, pp. 826-831. (Scopus). ISSN 1012-0386.
LAPIN, J. - GEBURA, M. - BAJANA, O. - PELACHOVÁ, T. - NAZMY, M. Effect of size and volume fraction of cuboidal γ' precipitates on mechanical properties of single crystal nickel-based superalloy CMSX-4. In KOVOVE MATER, 2009, vol 47, pp. 129-138. (Current Contents, Scopus, WOS). ISSN 0023-432X.
GEBURA, M. - LAPIN, J. Instability of γ/γ´ microstructure in a nickel-based single crystal superalloy during ageing. In TECHNOLÓGIA 2009. Ed.: Hrnčiar, V., Bratislava, STU, 2009, pp. 28-35. ISBN 978-80-227-3135-5.
GEBURA, M. - LAPIN, J. - TARABA, B. Microstructure degradation in notched nickel base single crystal superalloy CMSX-4 during creep. In The 14th International of PhD students’ seminar Semdok 2009, 2009, Proceedings, Ed.: EDIS, Žilina, pp. 17-21. ISBN 978-80-8070-959-4.
LAPIN, J. - GEBURA, M. - PELACHOVÁ, T. - BAJANA, O. Microstructure degradation of nickel base single crystal superalloy CMSX-4. In 18th International Conference on Metallurgy and Materials, METAL 2009 [online], 2009, Červený zámek, Hradec nad Moravicí, Tanger Ltd, pp. 304-310. (Scopus, WOS). ISBN:978-80-87294-10-9.
GEBURA, M. - LAPIN, J. Effect of multiaxial stress conditions on microstructure degradation of nickel base single crystal superalloy CMSX-4 during creep. In 18th International Conference on Metallurgy and Materials, METAL 2009, [online], 2009, Červený zámek, Hradec nad Moravicí, Tanger Ltd, pp. 311-317. (Scopus, WOS). ISBN:978-80-87294-10-9.
LAPIN, J. - GEBURA, M. - PELACHOVÁ, T. - NAZMY, M. Coarsening kinetics of cuboidal γ’ precipitates in single crystal nickel base superalloy CMSX-4. In KOVOVE MATER, 2008, vol.46, pp. 313-322. (Current Contents, Scopus, WOS). ISSN 0023-432X.
GEBURA, M. - LAPIN, J. Spontaneous rafting in single crystal Ni-base superalloy during long-term ageing. Materials Science and Technology [online], 2008, vol.4, pp. 32-38. ISSN 1335-9053.
GEBURA, M. - LAPIN, J. - PELACHOVÁ, T. Structure degradation development in nickel-based single crystal superalloy CMSX-4. In International Doctoral Seminar 2007 – Proceedings, 2007, AlumniPress, Trnava. ISBN 978-80-8096-011-7.
Súvisiace projekty
- Vplyv viacosovej napätosti na degradáciu mikroštruktúry niklových monokryštalických superzliatin v priebehu creepu, 2010 - 2012
- Vývoj a degradácia mikroštruktúry niklových zliatin v priebehu usmernenej kryštalizácie, tepelného spracovania a creepu, 2007 - 2009
- Vývoj a degradácia mikroštruktúry superzliatiny CMSX4 v priebehu starnutia a creepu, 2005 - 2008