Služby / Hodnotenie štruktúry materiálov /
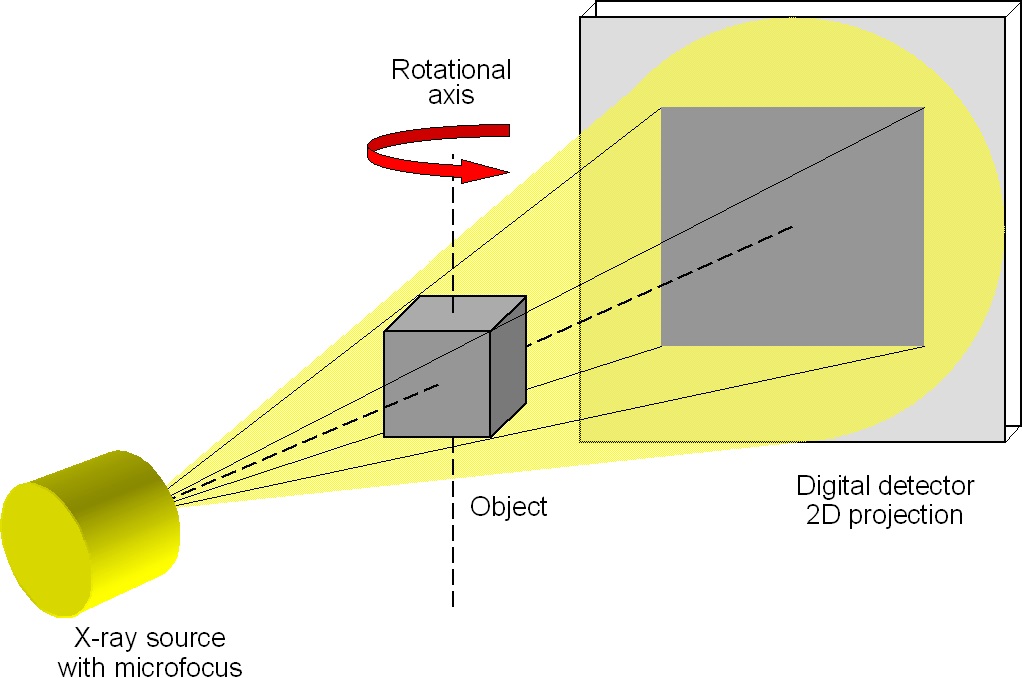 3D CT principle
3D CT principle
Usually, the object is rotated totally at 360° which allows 3-D reconstruction of the studied material. X-ray intensity depends on the sample thickness, the density and atomic number of the material. The resulting object is displayed in different grey values, which correspond to the different density of the material; high density leads to bright and low density to dark display.
Possibility of CT:
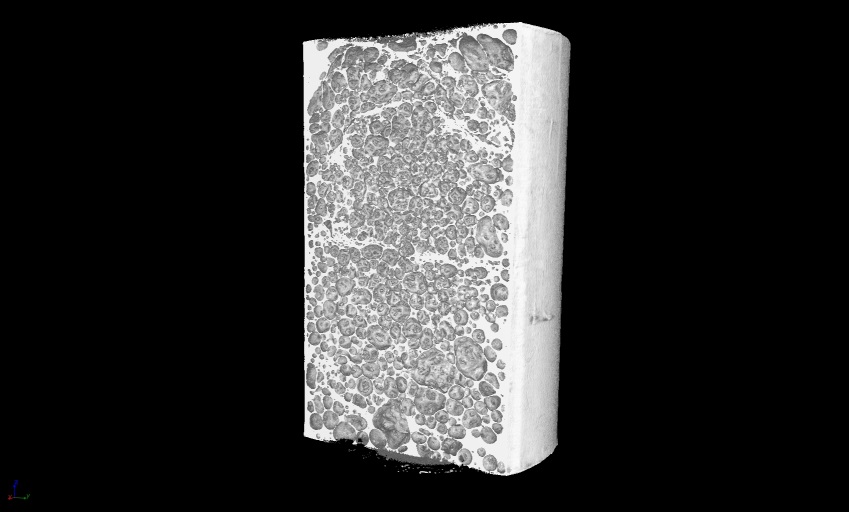 3D view
3D view
 x view
x view
 y view
y view
 z view
z view
Cloth
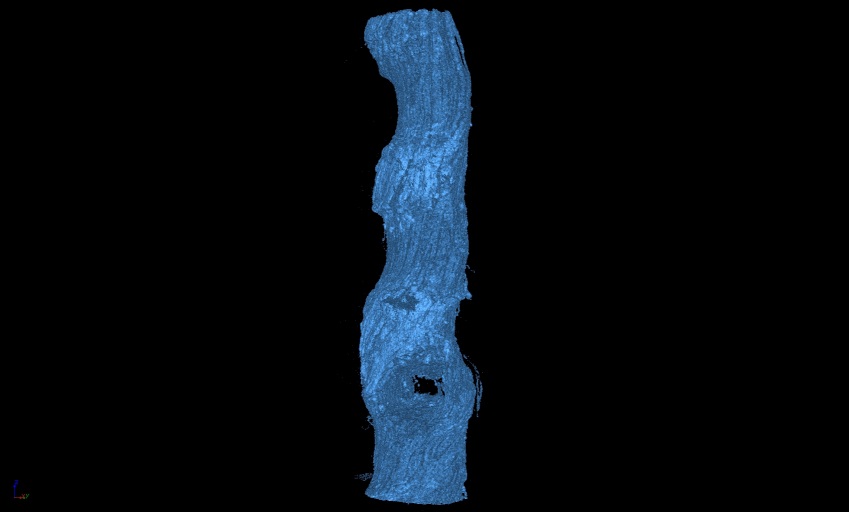 3D view
3D view
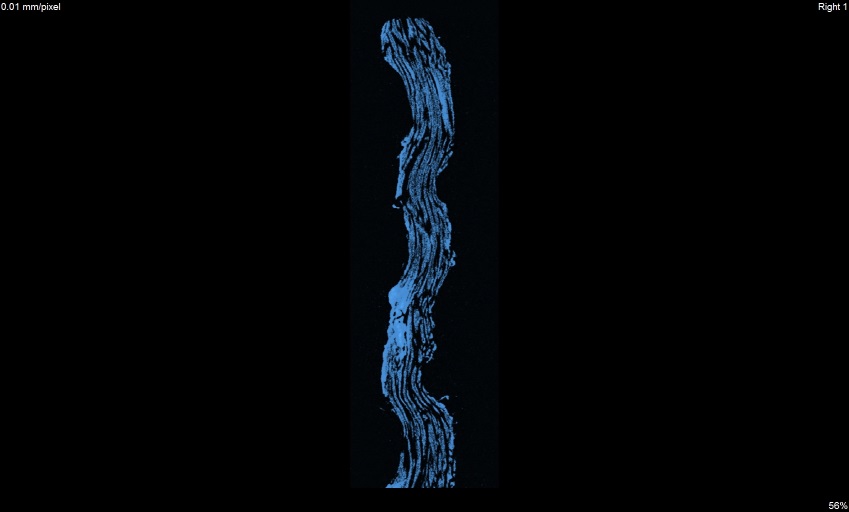 x view
x view
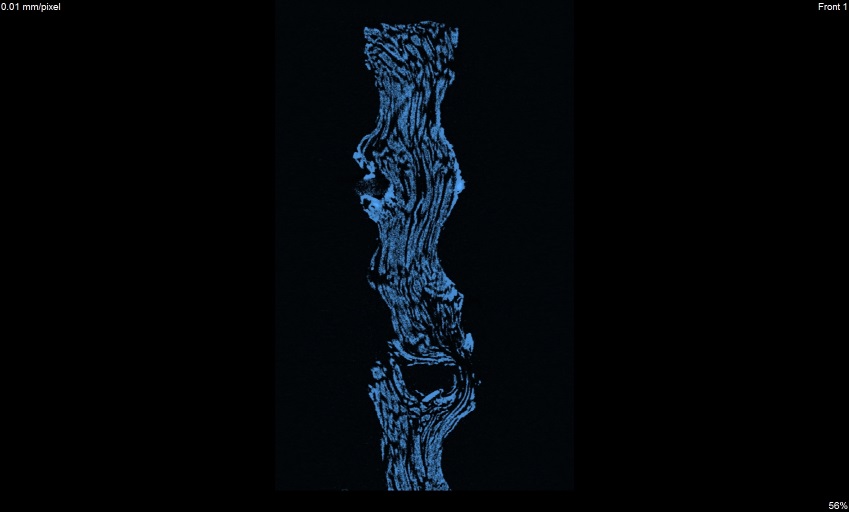 y view
y view
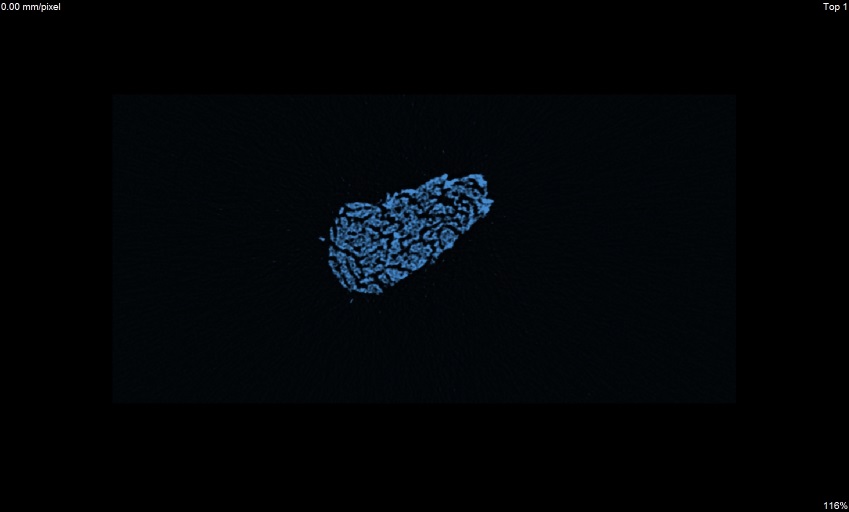 z view
z view
Segmentation of aluminium foam infiltrated by PCM
 3D view
3D view
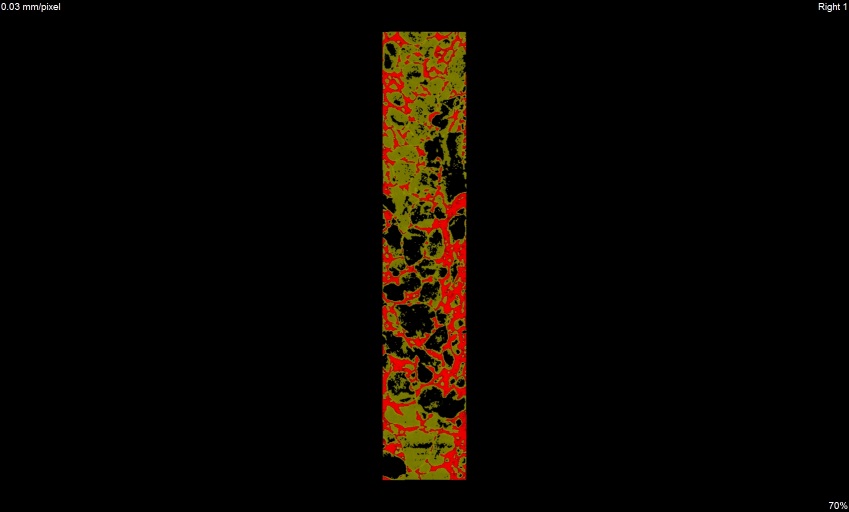 x view
x view
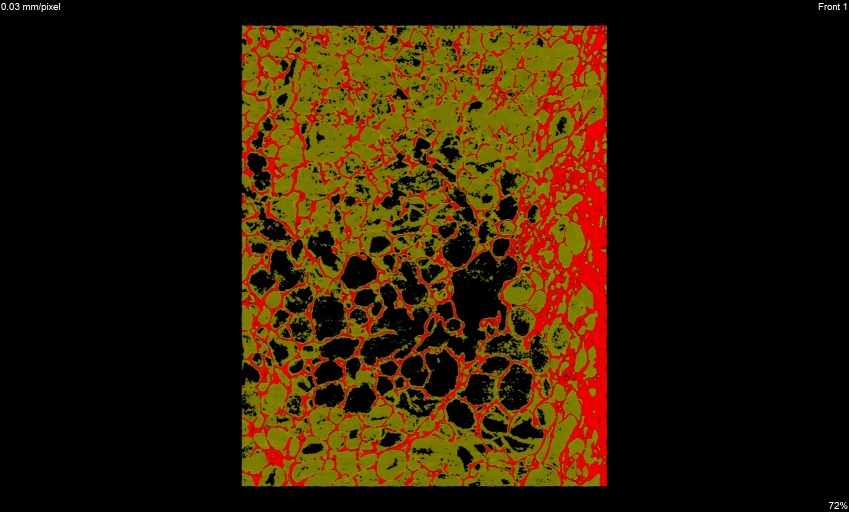 y view
y view
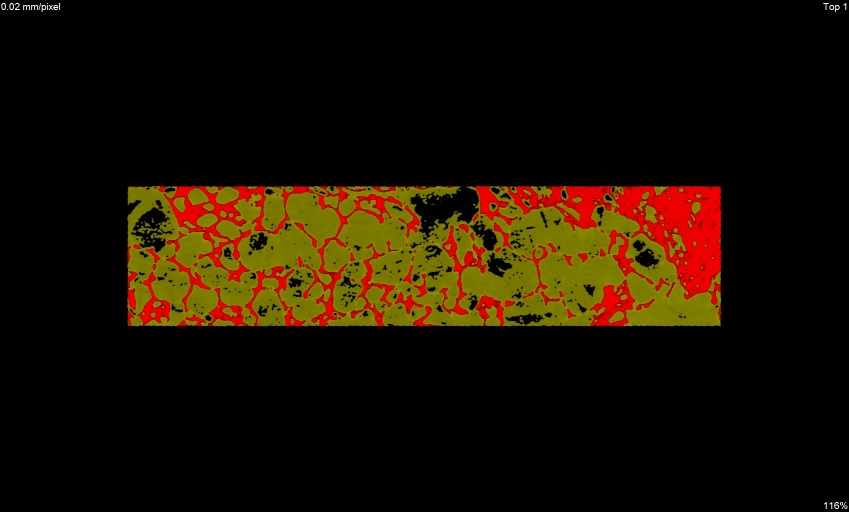 z view
z view
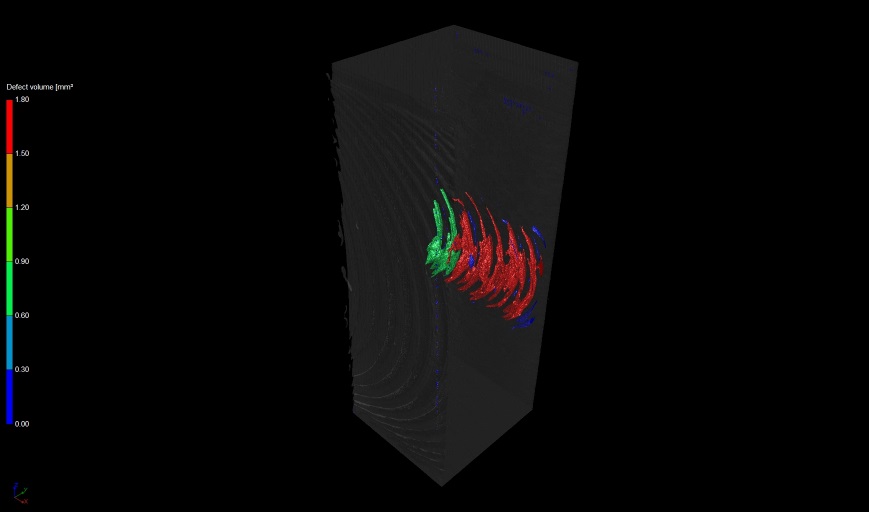 3D view
3D view
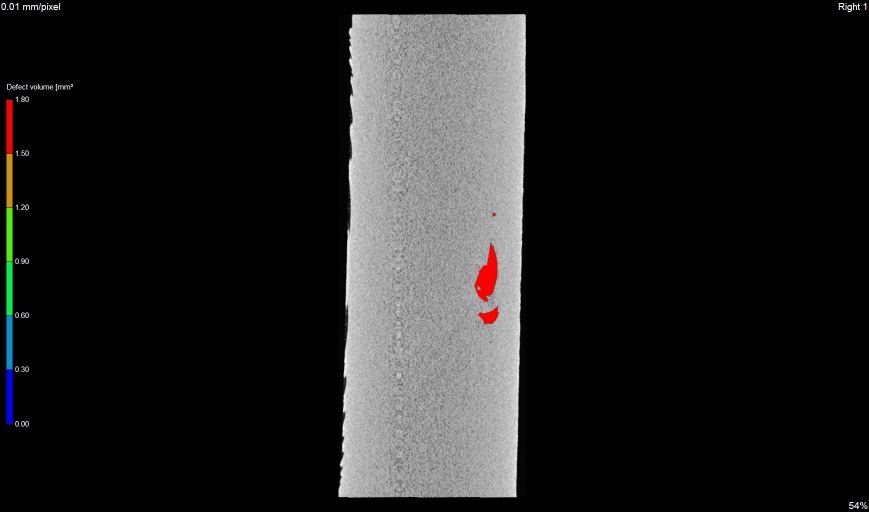 x view
x view
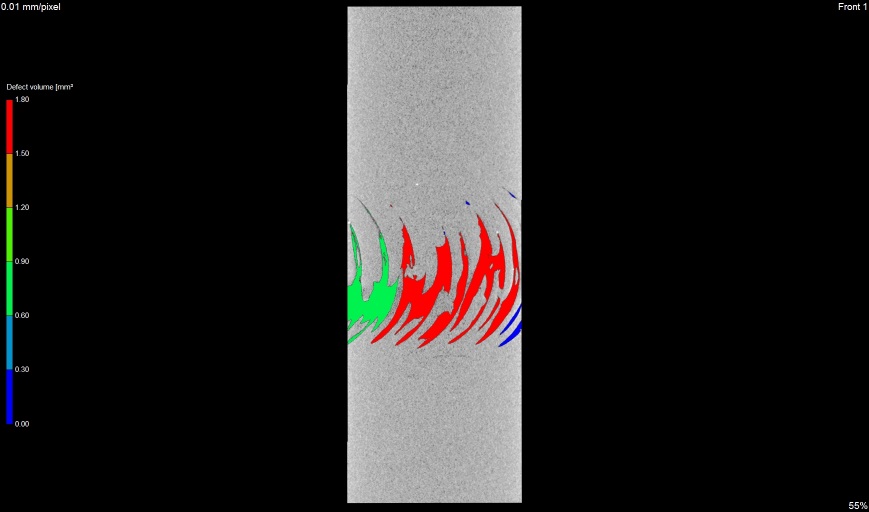 y view
y view
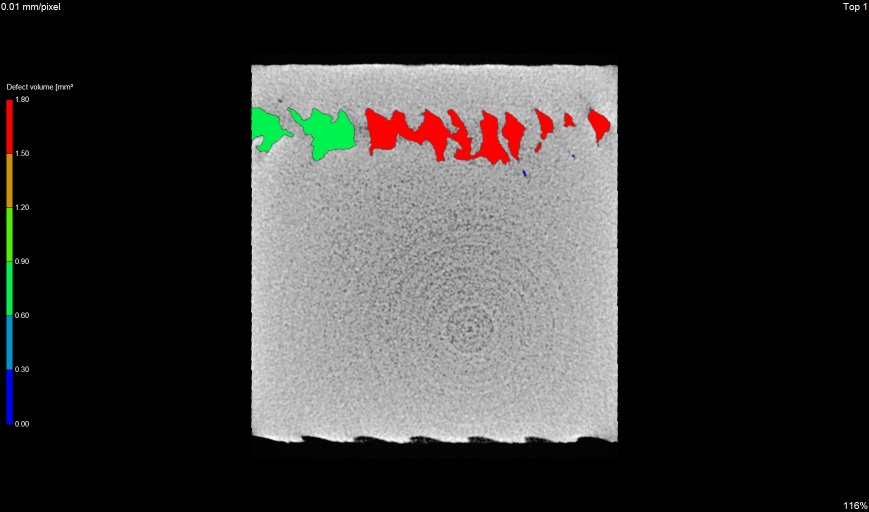 z view
z view
Deformation on the outer side of pipe
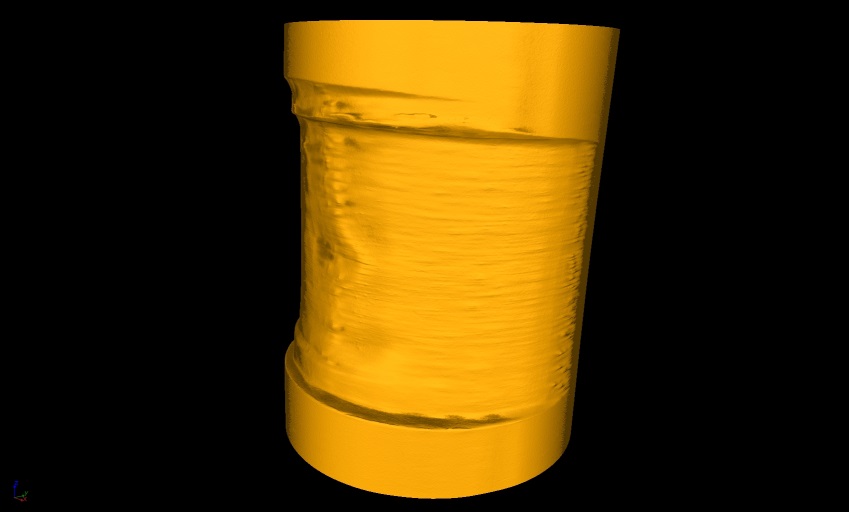 3D view
3D view
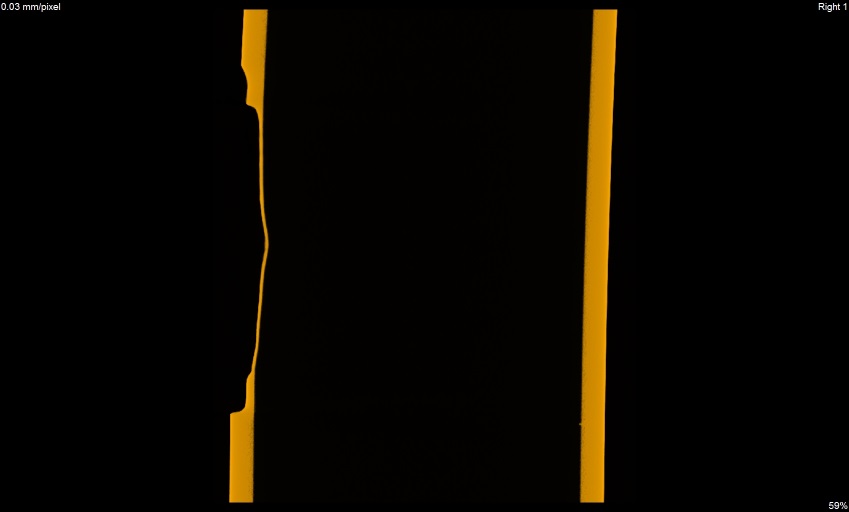 x view
x view
 y view
y view
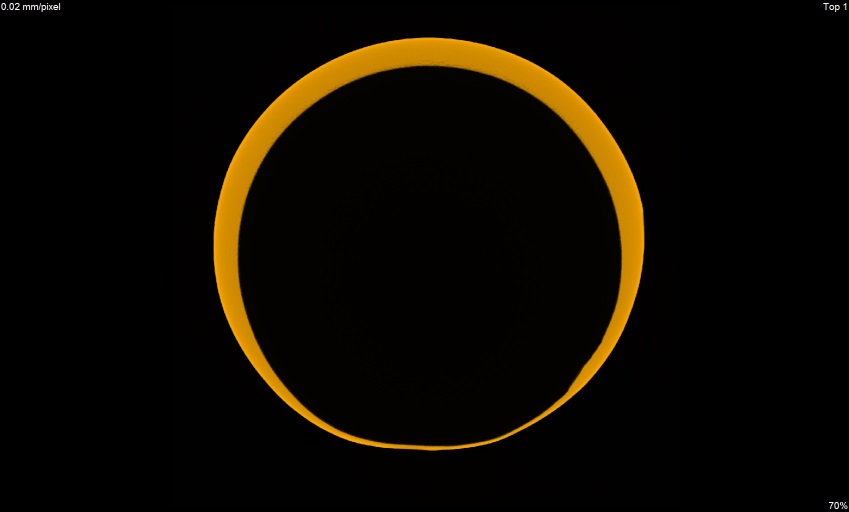 z view
z view
Crack in sprocket
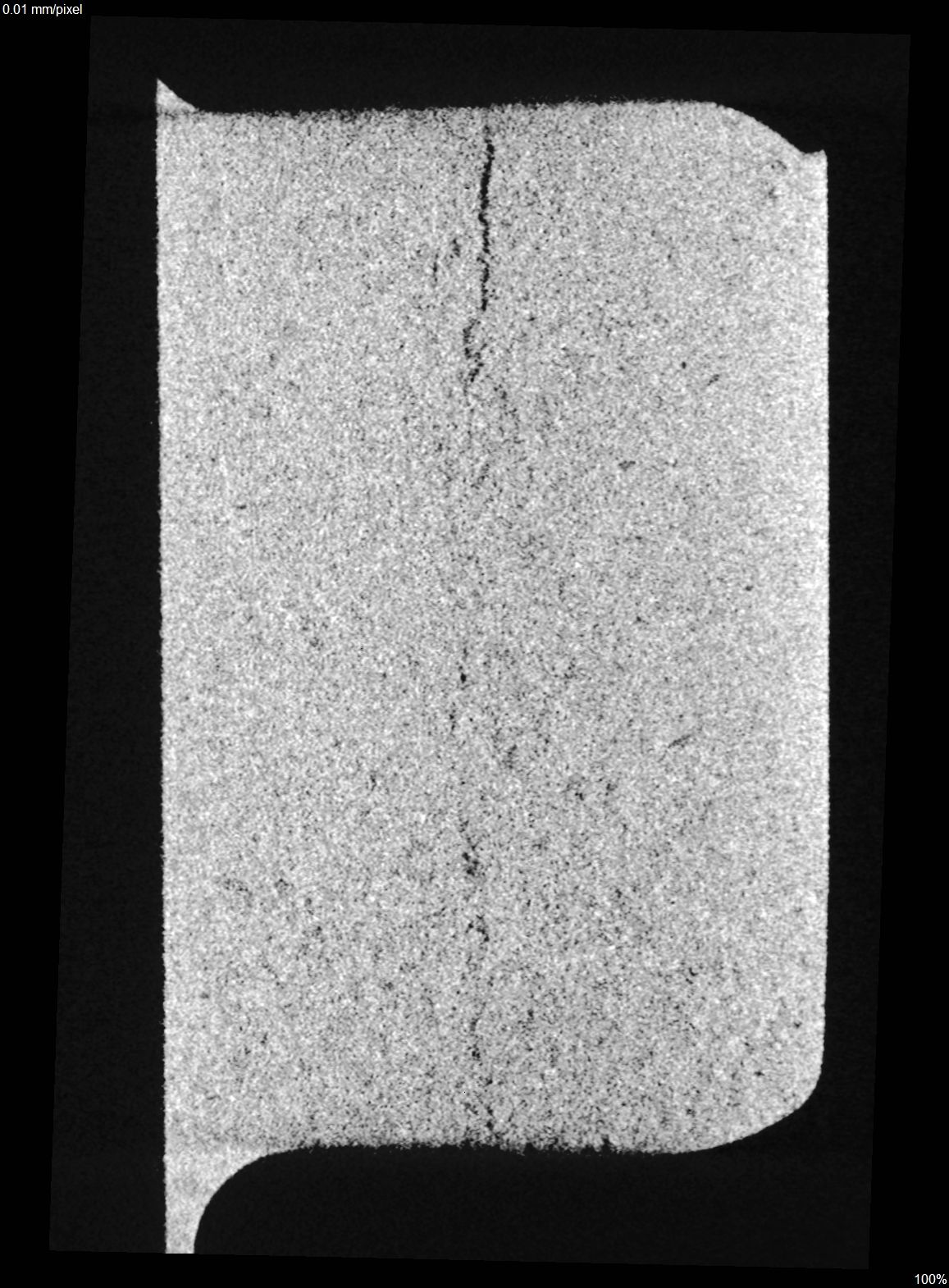

 3D view
3D view
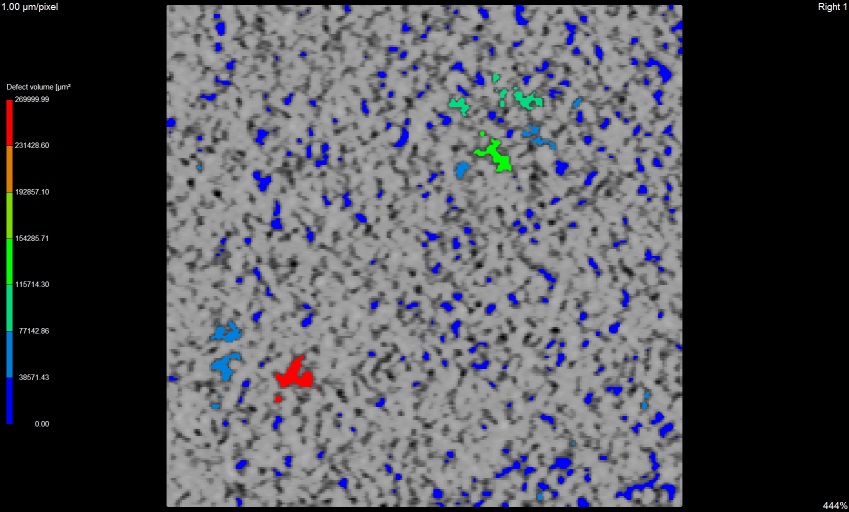 x view
x view
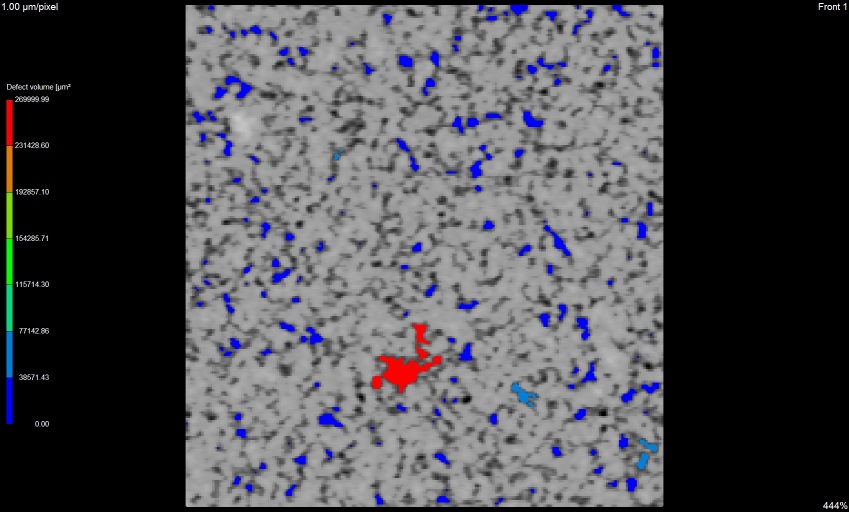 y view
y view
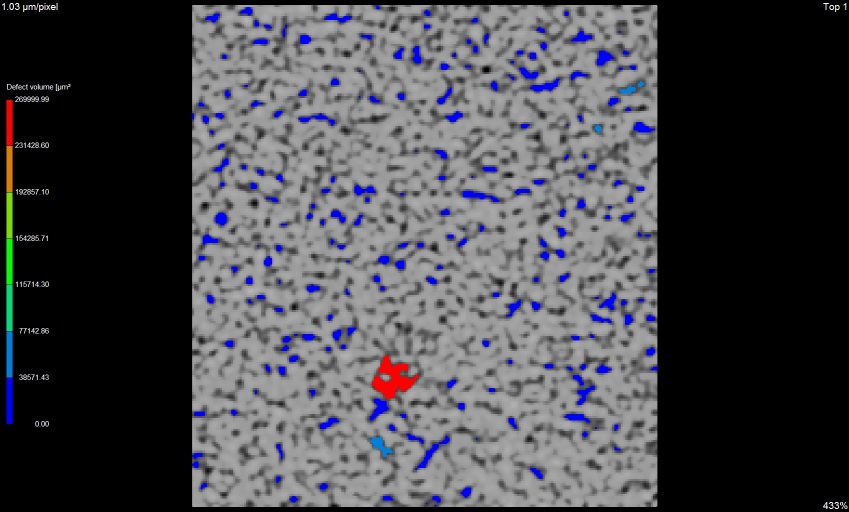 z view
z view
Peter Oslanec
Analýza defektov (vmestky, prímesy, póry, trhliny)
RTG tomografia
General purpose
Computed tomography (CT) is a non-destructive method for material testing with aim to reveal the inner structure of the materials without their destroying.Principle of operation
Non-destructive testing of materials using 3D tomography is composed of two steps - scanning and volume reconstruction. During scanning, radiation source, sample and detector are arranged in one plane/line. The sample is fixed in a holder, which is scanned during step-wise rotation about the axis of rotation at a small selected angle (e.g. 12´). The x-ray beam penetrates into the sample and interacts with it. The interacted signal is detected on the digital detector, which converts the x-ray intensity into a digital projection image. 3D CT principle
3D CT principleUsually, the object is rotated totally at 360° which allows 3-D reconstruction of the studied material. X-ray intensity depends on the sample thickness, the density and atomic number of the material. The resulting object is displayed in different grey values, which correspond to the different density of the material; high density leads to bright and low density to dark display.
Application of the technique
Computed tomography can be successfully used to study inner structure of materials in many fields of application, i.e. automotive industry, healthcare, geology, etc. The method allows studying wide range of materials for example: metals, plastics, wood, ceramics, minerals, bones, fossils.Possibility of CT:
- 3D analysis and material composition
- Structure and defect analysis
- Determination of density and porosity
- Surface extraction
- Wall thickness measurement
- Defect sizes measurement
Typical case studies
3D analysis and material composition
Aluminium foam 3D view
3D view x view
x view y view
y view z view
z view 3D view
3D view x view
x view y view
y view z view
z view 3D view
3D view x view
x view y view
y view z view
z viewStructure and defect analysis
Defects in the weld 3D view
3D view x view
x view y view
y view z view
z view 3D view
3D view x view
x view y view
y view z view
z view
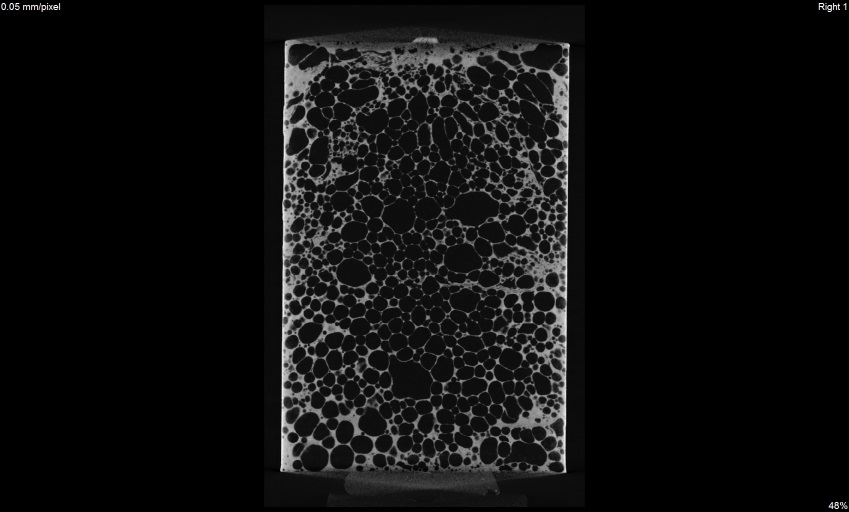
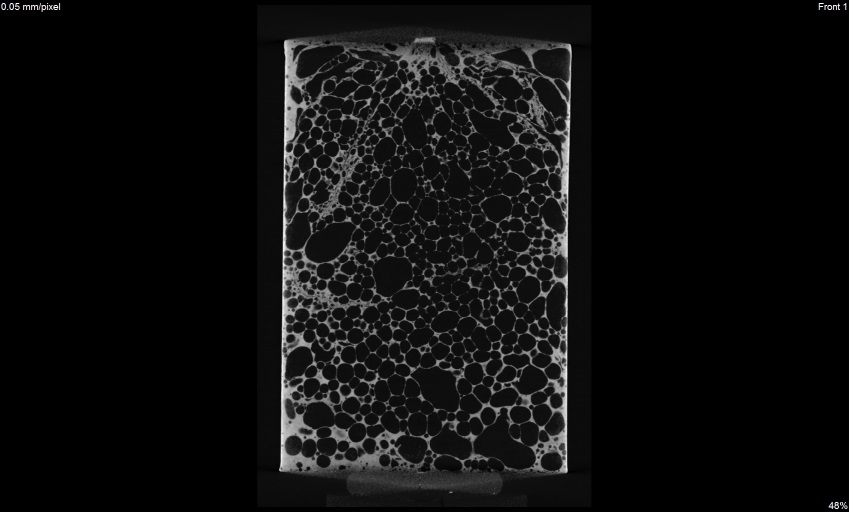
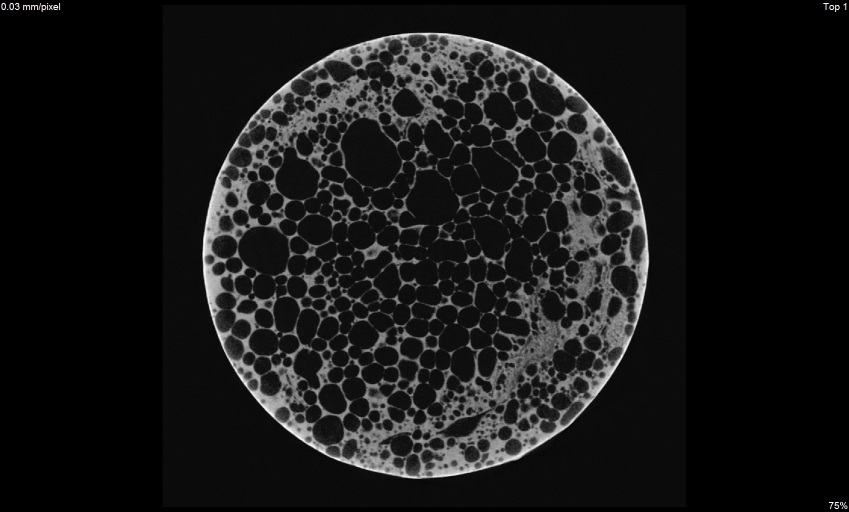
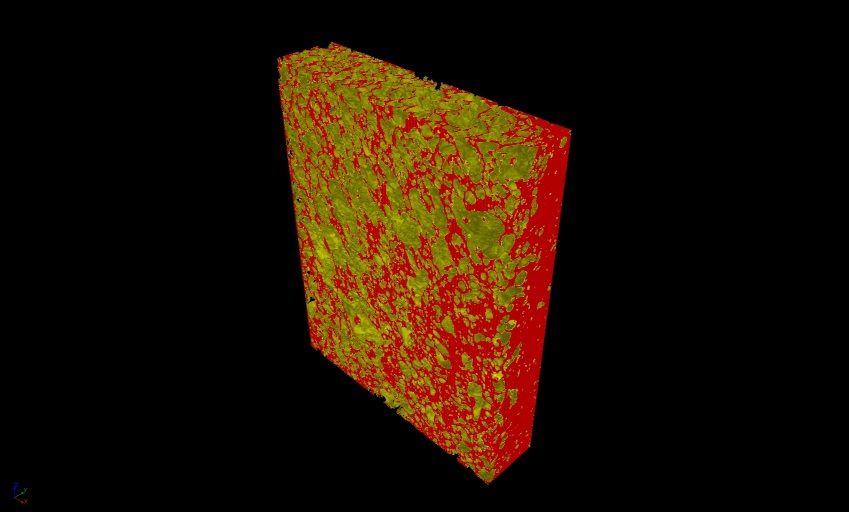
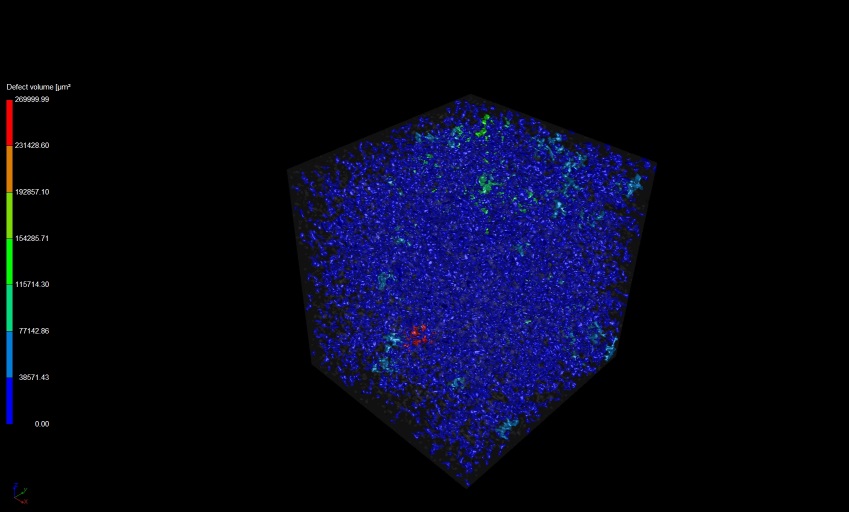
Determination of density and porosity
Porosity measurement 3D view
3D view x view
x view y view
y view z view
z viewZariadenia
- Phoenix/X-Ray Nanotom 180 (3D analysis and material composition, maximum power 15 W, minimum voxel size 0.5 µm, 12 bit Hamamatsu detector 2304 x 2304 pixel, pixel pitch 50 µm)
- Nikon XT H 225 ST (3D analysis and material composition, maximum power 225 W, focal spot size 3 µm up to 7 W, 14 bit flat panel, 2300 x 2300 active pixels, pixel size 127 µm)
- Nikon XT H 225 ST – additional filters (3D analysis and material composition, maximum power 225 W, maximum frame rate at 1x1 binning - 3 fps, 14 bit flat panel, 2300 x 2300 active pixels, pixel size 127 µm)
Kontakt
Tomáš DvorákPeter Oslanec