Microsegregation behaviour of main alloying elements in a peritectic TiAl based alloy
Summary
The effect of solidification parameters (growth rate V and temperature gradient G
L) and the effect of columnar to equiaxed transition (CET) on microsegregation behaviour of main alloying elements in peritecticTi-44Al-5Nb-0.2B-0.2C (at.%) alloy were studied.
Objectives and achievements
-
The effect of solidification parameters on microsegregation behaviour
The effect of solidification parameters such as growth rate V and temperature gradient G
L on microsegregation behaviour of main alloying elements was studied in the samples prepared by quench during directional solidification (QDS) at various combinations of V and G
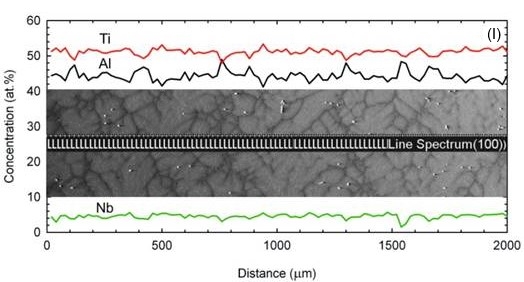
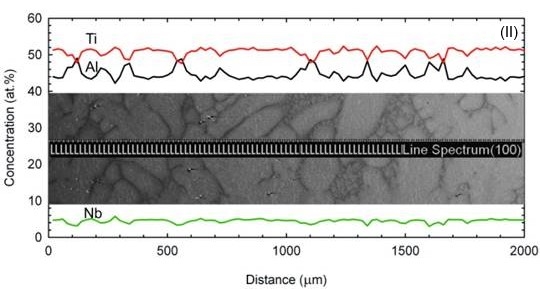
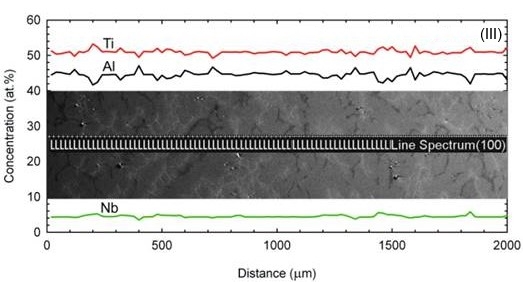
L. The studied alloy solidifies with β (Ti-based solid solution with cubic crystal structure) primary solidification phase and undergoes L + β → α peritectic transformation. The energy-dispersive spectrometry (EDS) analyses and calculated effective distribution coefficients for Al, Ti and Nb confirmed that the alloying elements such as Ti and Nb segregate predominantly into the β dendrites and Al into the interdendritic liquid during directional solidification. Formation of the peritectic α-phase (Ti-based solid solution with hexagonal crystal structure) leads to an intensive back-diffusion of the alloying elements. Boron segregates into interdendritic liquid where it forms (Ti,Nb)B particles with ribbon-like morphology. Severity of microsegregation expressed by segregation deviation parameter for aluminium decreases with increasing growth rate V in the mushy zone and only slightly increases below the mushy zone. Moderate decrease of segregation deviation parameter for aluminium with the increase of G
L is observed at all measured positions except the position located close to the dendrite tip.
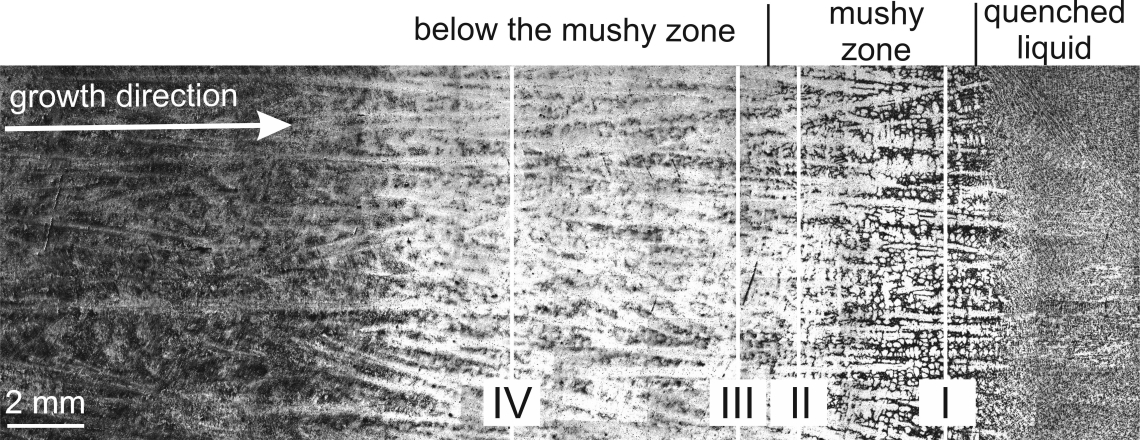

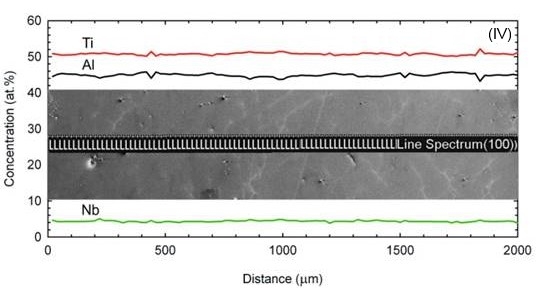
Distribution of Al, Ti and Nb in the QDS samples; Positions I, II, III, IV.
-
The effect of columnar to equiaxed transition on the microsegregation behaviour
The effect of columnar to equiaxed transition (CET) on the microsegregation behaviour of main alloying elements (Ti, Al and Nb) was studied in CET microstructures formed in cylindrical samples prepared by power down technique at a constant cooling rate a Bridgman type apparatus and in a large as-cast ingot. Microstructural analysis showed that the CET is not sharp but develops gradually during solidification in the studied alloy. A mixed zone (M) composed of columnar and equiaxed grains is formed between the columnar (C) and equiaxed (E) zones. The size of columnar and equiaxed grains depends on the position in the as-cast ingot. The severity of the microsegregation expressed by segregation deviation parameters calculated for Nb decreases from columnar to the equiaxed zone in the samples prepared by power down technique as well as in the as-cast ingot. While the calculated segregation deviation parameters for Al and Ti decrease from columnar to equiaxed zone in the samples prepared by power down technique, these parameters show no evolution with the local microstructure in the as-cast ingot. The calculated values of segregation deviation parameters for Al and Ti are significantly lower than those for Nb in all analyzed columnar, mixed and equiaxed zones of the samples.

CET in a sample prepared by power down technique
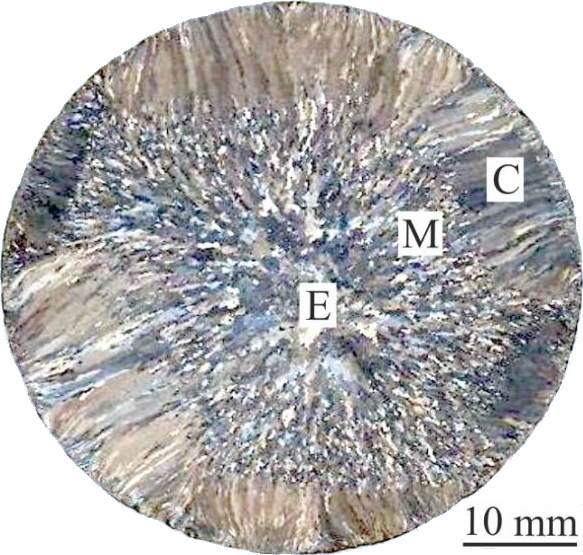
CET in the as-cast ingot
Additional reading
KLIMOVÁ, Alena - LAPIN, Juraj - PELACHOVÁ, Tatiana - NOSKO, Martin. Effect of solidification parameters on microsegregation behaviour of main alloying elements in a peritecticTiAl-basedalloy. In Kovové materiály, 2013, roč. 51, s. 89-99. (0.687 - IF2012). (2013 - CurrentContents, WOS, SCOPUS). ISSN 0023-432X.
LAPIN, Juraj - KLIMOVÁ, Alena - GABALCOVÁ, Zuzana. Effect of columnar to equiaxed transition on microsegregation behaviour of main alloying elements in peritecticTiAl-based alloy. In Kovové materiály, 2013, roč. 51, s. 147-154. (0.687 - IF2012). (2013 - CurrentContents, WOS, SCOPUS). ISSN 0023-432X.
Related projects

 CET in a sample prepared by power down technique
CET in a sample prepared by power down technique CET in the as-cast ingot
CET in the as-cast ingot